Alpha vs. Beta Glucose: Key Differences Explained

Glucose is a fundamental molecule in biology, serving as a primary source of energy for living organisms. However, not all glucose molecules are the same. Alpha glucose and beta glucose are two anomers of glucose that differ in their molecular structure, leading to distinct properties and functions. Understanding these differences is crucial for fields like biochemistry, nutrition, and medicine. In this post, we’ll explore the key distinctions between alpha and beta glucose, their roles in metabolism, and their significance in various applications. (glucose anomers, molecular structure, biochemistry)
What Are Alpha and Beta Glucose?

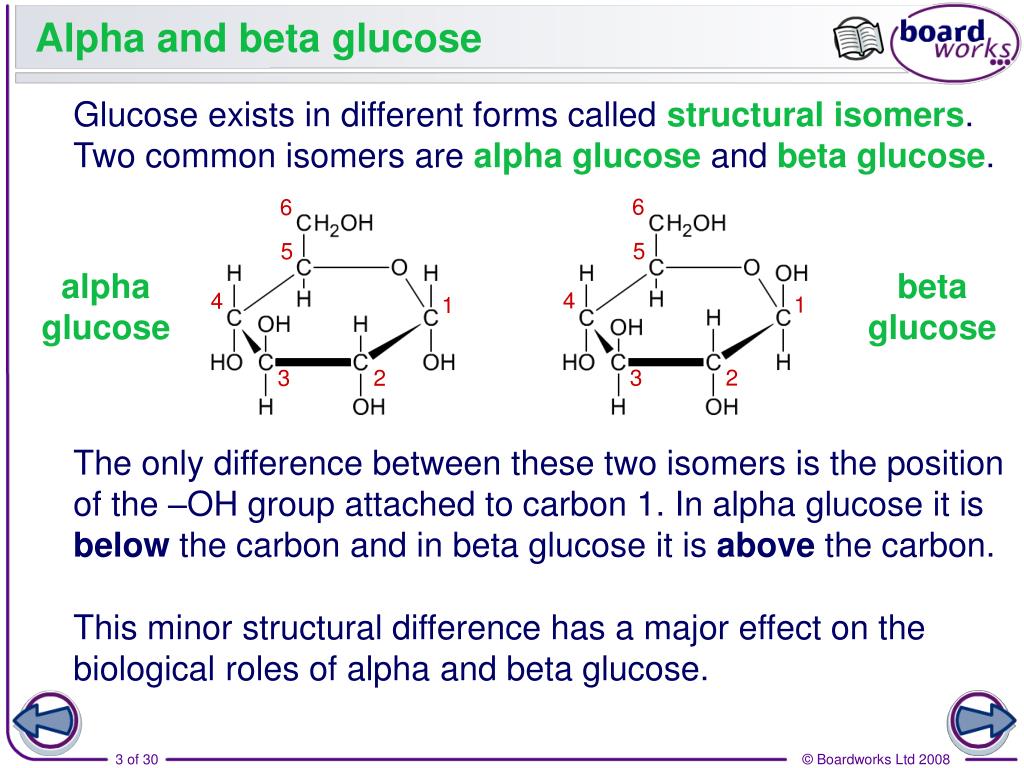
Alpha and beta glucose are stereoisomers of glucose, specifically anomers, which differ in the orientation of the hydroxyl group (-OH) at the first carbon atom (C1). This small structural difference results in significant variations in their chemical and biological behavior. (stereoisomers, anomers, chemical behavior)
Structural Differences
- Alpha Glucose: The -OH group at C1 is below the plane of the ring structure.
- Beta Glucose: The -OH group at C1 is above the plane of the ring structure.
| Property | Alpha Glucose | Beta Glucose |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation of -OH at C1 | Below the plane | Above the plane |
| Stability | Less stable | More stable |
| Occurrence in Nature | Less common | More common (e.g., cellulose) |

Roles in Metabolism and Biology

Both alpha and beta glucose play distinct roles in biological systems, particularly in energy storage and structural functions. (metabolism, energy storage, biological systems)
Alpha Glucose in Metabolism
Alpha glucose is a key component in glycogen, the primary storage form of glucose in animals. It is also the form of glucose found in maltose, a disaccharide derived from starch. (glycogen, maltose, starch)
Beta Glucose in Structural Roles
Beta glucose is a building block of cellulose, the structural component of plant cell walls. Its stability makes it ideal for forming strong, rigid structures. (cellulose, plant cell walls, structural stability)
💡 Note: While alpha glucose is more prevalent in animal metabolism, beta glucose dominates in plant biology due to its structural advantages.
Applications in Industry and Research
The unique properties of alpha and beta glucose make them valuable in various industries, from food production to pharmaceuticals. (industrial applications, food production, pharmaceuticals)
Alpha Glucose in Food Industry
Alpha glucose is used in the production of maltodextrin and high-fructose corn syrup, common sweeteners in processed foods. (maltodextrin, high-fructose corn syrup, processed foods)
Beta Glucose in Material Science
Beta glucose’s role in cellulose has inspired research into biomaterials and sustainable packaging, leveraging its strength and renewability. (biomaterials, sustainable packaging, renewability)
Key Takeaways Checklist
- Alpha glucose has the -OH group below the plane, while beta glucose has it above.
- Alpha glucose is prevalent in glycogen and maltose; beta glucose forms cellulose.
- Alpha glucose is less stable but more active in metabolism; beta glucose is stable and structural.
In summary, alpha and beta glucose are two anomers of glucose with distinct structures and functions. While alpha glucose is central to energy metabolism, beta glucose plays a crucial role in structural biology. Their differences highlight the versatility of glucose in both living organisms and industrial applications. Understanding these distinctions is essential for advancements in biochemistry, nutrition, and material science. (glucose anomers, biochemistry, nutrition, material science)
What is the main difference between alpha and beta glucose?
+
The main difference lies in the orientation of the -OH group at the C1 carbon atom. In alpha glucose, it is below the plane, while in beta glucose, it is above the plane.
Which form of glucose is more stable?
+
Beta glucose is more stable due to its structure, making it ideal for forming rigid structures like cellulose.
Why is alpha glucose important in metabolism?
+
Alpha glucose is a key component of glycogen, the primary energy storage molecule in animals, and is involved in the formation of maltose.



