APF of FCC: Understanding Face-Centered Cubic Structures
Understanding the Atomic Packing Factor (APF) of Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) structures is essential for materials science, engineering, and crystallography. The APF quantifies how efficiently atoms are packed within a crystal lattice, influencing properties like density, strength, and conductivity. FCC structures, common in metals like aluminum, copper, and gold, exhibit high symmetry and packing efficiency, making them a focal point in material design and analysis. This post explores the APF of FCC structures, its calculation, and its significance in various applications.
What is the Atomic Packing Factor (APF)?

The Atomic Packing Factor (APF) is a measure of the spatial arrangement of atoms in a crystal lattice. It represents the fraction of the unit cell volume occupied by atoms. For FCC structures, the APF is a key parameter, reflecting their efficient packing arrangement. Understanding APF helps in predicting material behavior, such as ductility, malleability, and thermal properties.
Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) Structures Explained

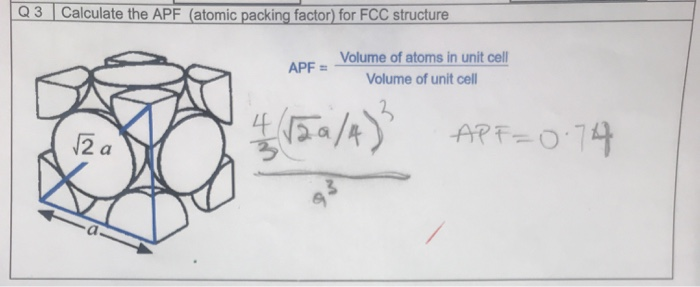
In FCC structures, atoms are arranged at the corners and center of each face of a cube. This arrangement maximizes space utilization, resulting in an APF of 0.74, one of the highest among crystal structures. FCC lattices are characterized by their close-packed planes, which contribute to their excellent mechanical properties.
Key Features of FCC Structures
- High Symmetry: FCC structures exhibit identical atomic arrangements along all axes.
- Close Packing: Atoms are tightly packed, minimizing voids within the lattice.
- Slip Systems: Multiple slip planes allow for easy deformation, making FCC metals highly ductile.
Calculating APF for FCC Structures

The APF for FCC structures can be calculated using the formula:
| Formula | APF = (Number of Atoms × Volume of Atom) / Volume of Unit Cell |
|---|

For FCC, each unit cell contains 4 atoms. The calculation involves the radius of the atom (r) and the edge length of the unit cell (a), where a = 2√2r. Substituting these values yields an APF of 0.74, highlighting the efficiency of FCC packing.
Steps to Calculate APF
- Determine the number of atoms per unit cell (4 for FCC).
- Calculate the volume of one atom using the formula (4/3)πr³.
- Find the volume of the unit cell using a³, where a = 2√2r.
- Apply the APF formula to obtain the packing efficiency.
💡 Note: The APF calculation assumes spherical atoms with no interstitial voids, which is a simplification for theoretical purposes.
Significance of APF in Material Science

The APF of FCC structures plays a critical role in determining material properties. High APF values correlate with greater density and strength, making FCC metals ideal for structural applications. For instance, aluminum (FCC) is widely used in aerospace due to its lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio.
Applications of FCC Materials
- Aerospace: Aluminum and titanium alloys for aircraft components.
- Electronics: Copper and gold for wiring and connectors.
- Jewelry: Gold and silver for decorative items.
Summary and Checklist

To summarize, the APF of FCC structures is a vital metric for understanding atomic arrangement and material properties. Here’s a quick checklist for key takeaways:
- FCC structures have an APF of 0.74, indicating high packing efficiency.
- The APF calculation involves atomic volume and unit cell volume.
- FCC materials are widely used in aerospace, electronics, and jewelry.
By mastering the APF of FCC structures, engineers and scientists can optimize material performance for diverse applications. Whether designing alloys or analyzing crystal structures, understanding APF is indispensable. (Crystal Structures,Material Science,Packing Efficiency)
What is the APF of an FCC structure?
+The APF of an FCC structure is 0.74, indicating 74% of the unit cell volume is occupied by atoms.
Why are FCC structures preferred in material science?
+FCC structures offer high packing efficiency, ductility, and strength, making them ideal for various applications.
How does APF affect material properties?
+Higher APF values generally correlate with greater density, strength, and conductivity in materials.



