Understanding ATM in SI Units: A Quick Guide

Understanding ATM in SI Units: A Quick Guide
If you’ve ever wondered about the SI units used in ATM (Automated Teller Machine) technology, you’re not alone. ATM systems rely on precise measurements for functionality, security, and user experience. This guide breaks down ATM in SI units, focusing on key metrics like voltage, current, and data transfer rates. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or a professional in the banking sector, this post will help you grasp the essentials.
What Are SI Units and Why Do They Matter in ATM Systems?

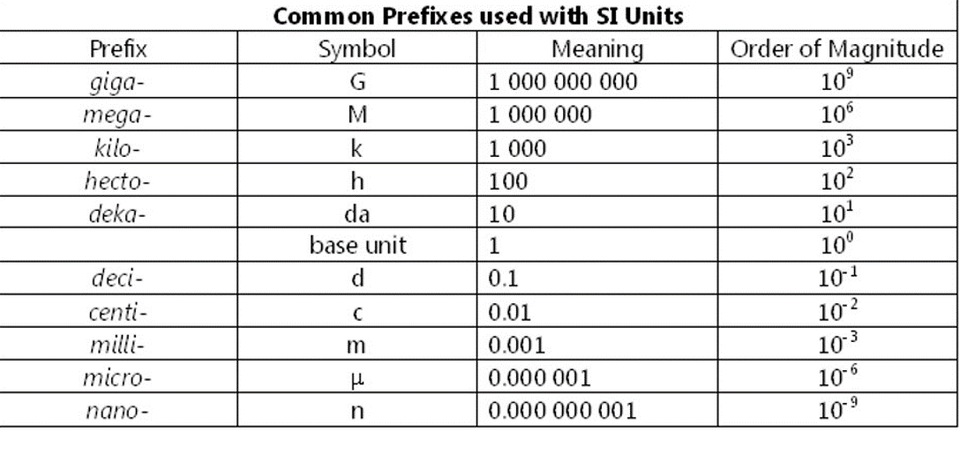
SI units, or the International System of Units, are the standard for measuring physical quantities globally. In ATM technology, SI units ensure consistency in electrical parameters, data transmission, and safety compliance. For instance, voltage is measured in volts (V), current in amperes (A), and data transfer rates in bits per second (bps). Understanding these units is crucial for troubleshooting, maintenance, and upgrading ATM systems.
Key SI Units in ATM Technology
1. Electrical Parameters
ATMs operate on specific electrical inputs to function efficiently. Here are the primary SI units involved:
- Voltage (V): Most ATMs run on a standard voltage range of 100–240 V.
- Current (A): Typical current consumption ranges from 2–5 A, depending on the model.
- Power (W): Power consumption is measured in watts, usually between 200–500 W.
📌 Note: Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for exact electrical requirements.
2. Data Transfer Rates
ATMs rely on secure and fast data transmission for transactions. SI units for data transfer include:
- Bits per second (bps): Basic unit for measuring data speed.
- Kilobits per second (Kbps) and Megabits per second (Mbps): Commonly used for ATM networks.
| Parameter | SI Unit | Typical ATM Value |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Volts (V) | 100–240 V |
| Current | Amperes (A) | 2–5 A |
| Data Transfer Rate | Megabits per second (Mbps) | 1–10 Mbps |

Practical Applications of SI Units in ATMs
Understanding SI units is not just theoretical; it has practical implications for ATM maintenance and upgrades. For example, knowing the power consumption in watts helps in selecting the right UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) for uninterrupted operation. Similarly, data transfer rates in Mbps ensure that transaction processing remains swift and secure.
Checklist for ATM Maintenance Using SI Units
- Verify voltage and current inputs match the ATM’s specifications.
- Monitor power consumption to prevent overheating.
- Test data transfer rates to ensure fast and secure transactions.
- Inspect cables and connectors for wear and tear.
By mastering SI units in ATM technology, you can enhance the efficiency and reliability of these essential banking devices. (ATM maintenance, SI units in banking, ATM technology)
What are SI units?
+SI units, or the International System of Units, are the standard measurements used globally for physical quantities.
Why are SI units important in ATM systems?
+SI units ensure consistency in electrical parameters, data transmission, and safety compliance in ATM technology.
What is the typical voltage range for ATMs?
+Most ATMs operate within a voltage range of 100–240 V.
In summary, SI units play a vital role in ATM technology, ensuring precise measurements for electrical parameters and data transfer rates. By understanding these units, you can effectively maintain and optimize ATM systems for better performance and reliability. Whether you’re a technician or a banking professional, this knowledge is invaluable for your work. (ATM technology, SI units, banking systems)