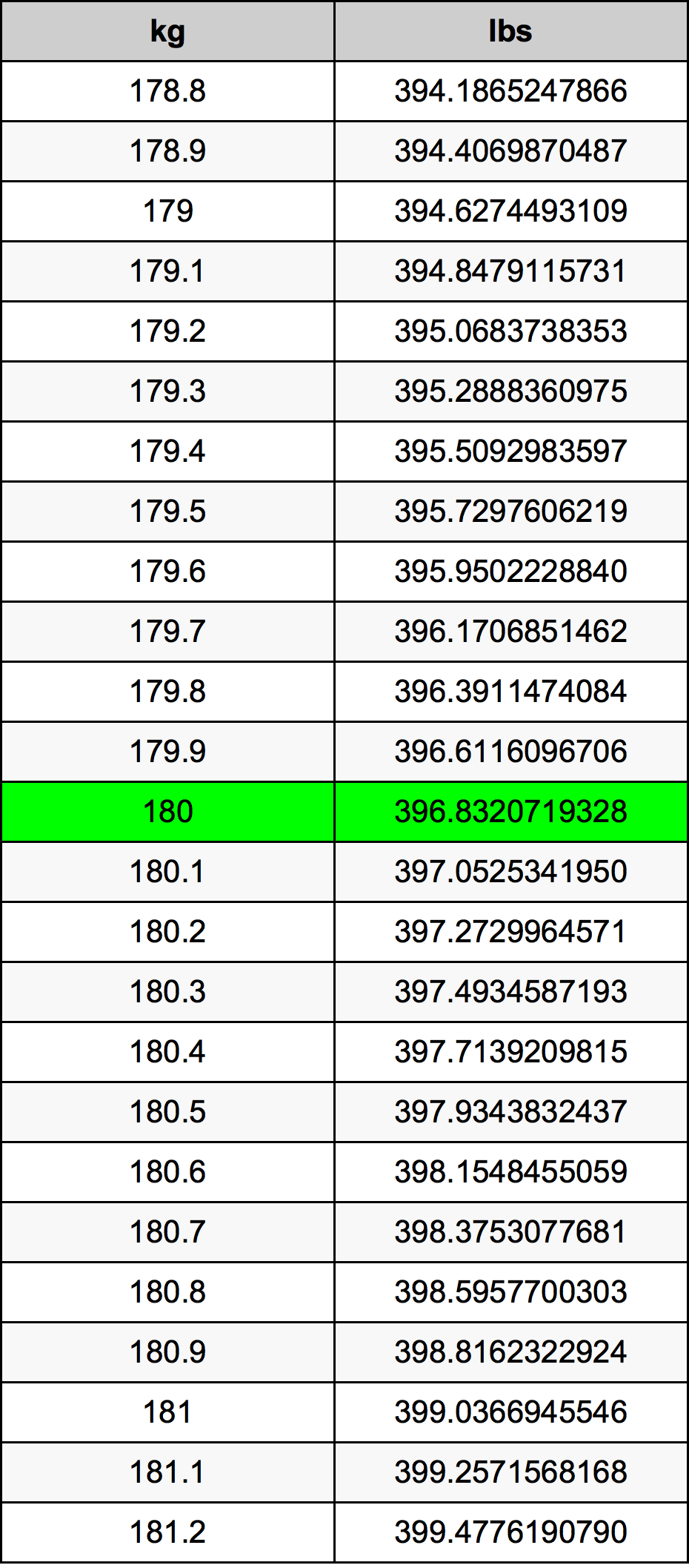
Bohr Model of Fluorine: A Simple Atomic Structure Explained

The Bohr model of fluorine is a fundamental concept in chemistry that simplifies the understanding of atomic structure. By visualizing the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus, this model provides a clear picture of how fluorine, a highly reactive element, behaves. Whether you’re a student, educator, or simply curious about atomic structures, this guide breaks down the Bohr model of fluorine into digestible parts.
Understanding the Bohr Model of Fluorine

The Bohr model is a theoretical framework introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913. It describes atoms as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons in specific energy levels or shells. For fluorine, an element with atomic number 9, the Bohr model illustrates its electron configuration in a straightforward manner.
Key Components of the Bohr Model
- Nucleus: Contains protons and neutrons. Fluorine has 9 protons and 10 neutrons.
- Electron Shells: Electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed shells. Fluorine has two shells: the first shell (K) holds 2 electrons, and the second shell (L) holds 7 electrons.
- Electron Configuration: Represented as 2-7, indicating the number of electrons in each shell.
📌 Note: The Bohr model is a simplified representation and does not account for more complex quantum mechanics principles.
Why Fluorine’s Bohr Model Matters

Fluorine’s Bohr model is crucial for understanding its chemical properties. With 7 valence electrons, fluorine is highly reactive and tends to gain one electron to achieve a stable octet. This explains its role in forming compounds like sodium fluoride (NaF) and its use in industries such as dentistry and water treatment.
Practical Applications of Fluorine
- Dental Health: Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel, preventing cavities.
- Water Treatment: Fluorine compounds are added to drinking water to improve dental health.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Used in producing plastics, pesticides, and refrigerants.
How to Draw the Bohr Model of Fluorine

Drawing the Bohr model of fluorine is a simple process. Follow these steps:
- Draw the Nucleus: Represent the nucleus with a circle and label it with 9 protons and 10 neutrons.
- Add Electron Shells: Draw two concentric circles around the nucleus for the K and L shells.
- Place Electrons: Place 2 electrons in the K shell and 7 electrons in the L shell.
✏️ Note: Electrons should be evenly spaced in each shell for clarity.
Comparing Bohr Model and Modern Atomic Theory

While the Bohr model is a foundational concept, modern atomic theory provides a more accurate representation of electron behavior. Key differences include:
| Aspect | Bohr Model | Modern Atomic Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Electron Orbits | Fixed circular orbits | Probabilistic electron clouds |
| Energy Levels | Discrete shells | Sublevels and orbitals |

Checklist for Mastering the Bohr Model of Fluorine

- Understand the basic structure of the Bohr model.
- Memorize fluorine’s electron configuration (2-7).
- Practice drawing the model accurately.
- Explore real-world applications of fluorine.
The Bohr model of fluorine offers a clear and accessible way to understand this element’s atomic structure. By grasping its components and applications, you’ll gain valuable insights into chemistry and its practical uses. Whether for academic purposes or personal curiosity, this model is a stepping stone to deeper scientific exploration.
What is the Bohr model of fluorine?
+The Bohr model of fluorine depicts its atomic structure with a nucleus containing 9 protons and 10 neutrons, surrounded by two electron shells holding 2 and 7 electrons, respectively.
Why does fluorine have 7 valence electrons?
+Fluorine has 7 valence electrons in its outer shell (L shell), which makes it highly reactive and eager to gain one more electron to achieve a stable octet.
How does the Bohr model differ from modern atomic theory?
+The Bohr model uses fixed electron shells, while modern atomic theory describes electrons in probabilistic clouds and includes sublevels and orbitals.
atomic structure, electron configuration, chemical properties, Bohr model, fluorine,atomic structure, electron configuration, chemical properties, Bohr model, fluorine