Boron-10: Protons, Neutrons, Electrons Explained

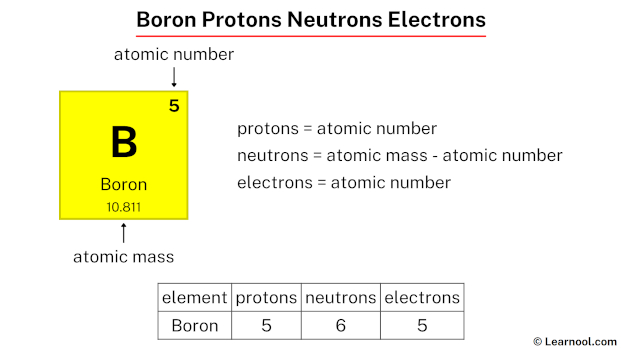
Boron-10 is a unique isotope of boron, widely recognized for its applications in nuclear technology, medicine, and materials science. With an atomic number of 5, boron-10 consists of 5 protons, 5 neutrons, and 5 electrons, making it a fascinating subject for both informational and commercial audiences. This blog post will delve into the composition of boron-10, its properties, and its practical uses, ensuring you gain a comprehensive understanding of this essential isotope.
What is Boron-10? (Boron Isotopes, Atomic Structure)
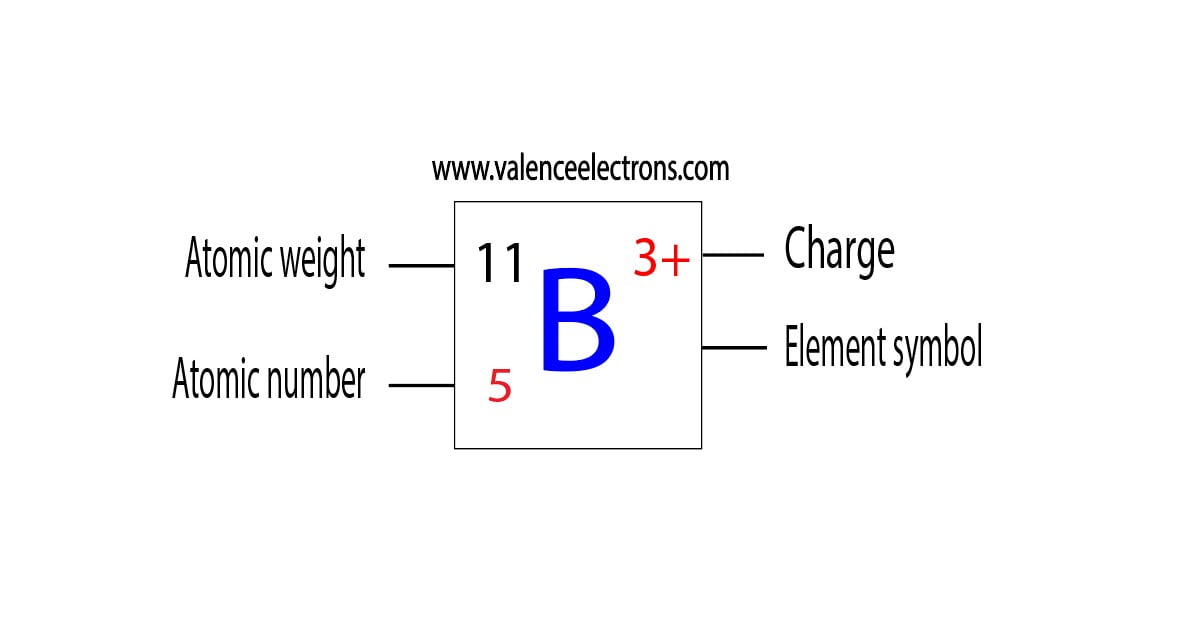
Boron-10 is one of the two stable isotopes of boron, the other being boron-11. Its atomic structure is defined by its protons, neutrons, and electrons. Understanding these subatomic particles is crucial to grasping boron-10’s significance in various fields.
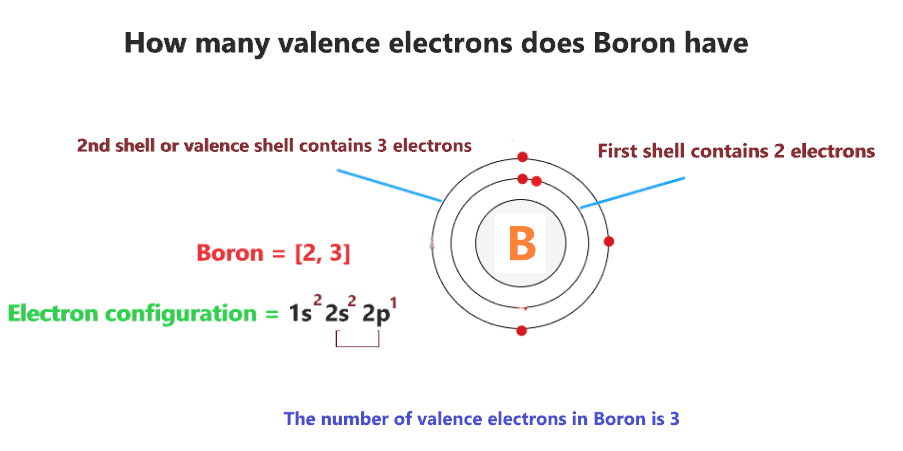
Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons in Boron-10 (Subatomic Particles, Atomic Composition)
- Protons: Boron-10 has 5 protons, determining its atomic number and classification as boron.
- Neutrons: It contains 5 neutrons, contributing to its mass number of 10.
- Electrons: With 5 electrons, boron-10 maintains a neutral charge in its ground state.
This balanced atomic structure makes boron-10 a stable and versatile isotope, ideal for specialized applications.
Applications of Boron-10 (Nuclear Technology, Medical Uses)
Boron-10’s unique properties make it invaluable in several industries. Its ability to absorb neutrons efficiently is particularly noteworthy.
Nuclear Technology and Boron-10 (Neutron Absorption, Nuclear Reactors)
In nuclear reactors, boron-10 is used as a neutron absorber to control the fission process. Its high neutron-capture cross-section ensures safety and efficiency in reactor operations.
📌 Note: Boron-10’s neutron absorption capability is critical for preventing nuclear chain reactions from becoming uncontrollable.
Medical Applications of Boron-10 (Boron Neutron Capture Therapy, BNCT)
Boron-10 plays a pivotal role in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT), a cancer treatment method. When boron-10 is introduced into cancer cells and exposed to neutrons, it releases high-energy particles that destroy the cancerous tissue while sparing healthy cells.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Nuclear Reactors | Neutron absorption for reactor control |
| Cancer Treatment (BNCT) | Targeted therapy for malignant tumors |
| Materials Science | Enhances properties of composites and alloys |

How to Source Boron-10 (Boron Suppliers, Industrial Applications)
For commercial purposes, sourcing high-purity boron-10 is essential. Reputable suppliers offer enriched boron-10 for industrial and research applications.
✨ Note: Ensure suppliers provide certified purity levels to meet specific application requirements.
Checklist for Sourcing Boron-10 (Boron-10 Suppliers, Quality Assurance)
- Verify supplier credentials and certifications.
- Check boron-10 enrichment levels.
- Ensure compliance with industry standards.
- Assess packaging and shipping safety protocols.
Boron-10's unique atomic structure and properties make it an indispensable isotope in nuclear technology, medicine, and materials science. Whether you're exploring its informational aspects or seeking commercial applications, understanding its protons, neutrons, and electrons is key to unlocking its potential. From neutron absorption in reactors to groundbreaking cancer treatments, boron-10 continues to shape advancements across industries. (Boron-10 Applications, Atomic Structure, Nuclear Technology)
What makes boron-10 unique compared to boron-11?
+
Boron-10 has 5 neutrons, while boron-11 has 6, giving it a higher mass number and different nuclear properties.
How is boron-10 used in cancer treatment?
+
Boron-10 is used in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT), where it selectively targets and destroys cancer cells when exposed to neutrons.
Can boron-10 be used in everyday products?
+
While boron-10 is primarily used in specialized fields, boron compounds are found in everyday items like fiberglass and detergents.



