Calcium Sulfide: Ionic or Covalent? The Answer Revealed
Calcium sulfide, a compound with the formula CaS, often sparks curiosity about its chemical nature. Is it ionic or covalent? Understanding its bonding type is crucial for applications in industries like agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. This post delves into the characteristics of calcium sulfide, clarifying its classification and exploring its properties and uses.
Understanding Chemical Bonding: Ionic vs. Covalent
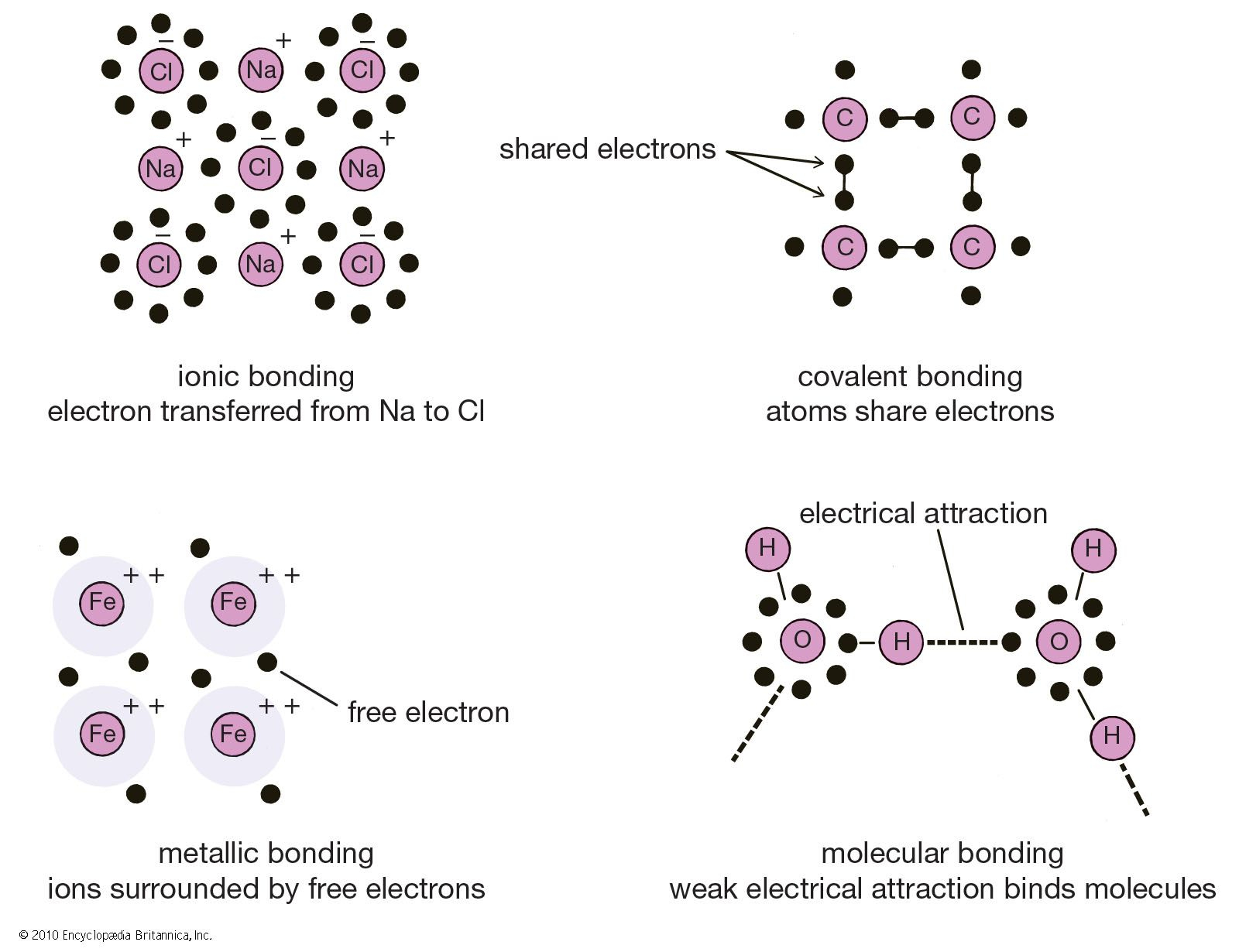
Chemical compounds are classified based on the type of bonds they form. Ionic bonds occur when electrons are transferred between atoms, creating charged ions that attract each other. Covalent bonds, on the other hand, involve shared electrons between atoms.
Key Differences Between Ionic and Covalent Compounds
- Ionic Compounds: High melting points, conduct electricity in molten or aqueous states, and are often solids at room temperature.
- Covalent Compounds: Lower melting points, poor electrical conductivity, and can exist as gases, liquids, or soft solids.
Calcium Sulfide: Analyzing Its Bonding

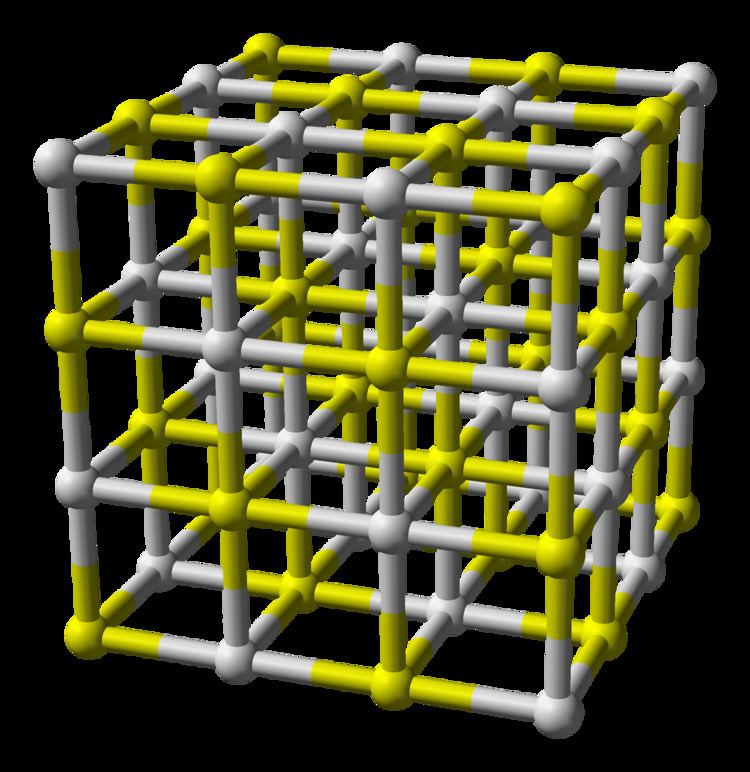
Calcium sulfide is formed between calcium (Ca), an alkaline earth metal, and sulfur (S), a nonmetal. The interaction between these elements is primarily ionic.
Why Calcium Sulfide is Ionic
- Electronegativity Difference: Calcium has a low electronegativity (1.0), while sulfur has a higher value (2.6). The significant difference (>1.7) indicates an ionic bond.
- Crystal Structure: Calcium sulfide exists as a crystal lattice, a hallmark of ionic compounds.
- Properties: It has a high melting point (2500°C) and conducts electricity when molten, typical of ionic substances.
📌 Note: While calcium sulfide is predominantly ionic, it may exhibit slight covalent character due to sulfur’s ability to form polar bonds.
Properties and Applications of Calcium Sulfide
Calcium sulfide’s ionic nature influences its properties and uses across various fields.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Appearance: White to yellow solid.
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, decomposes in acids.
- Reactivity: Reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen sulfide.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
- Agriculture: Used in fertilizers to provide sulfur and calcium to plants.
- Pharmaceuticals: A component in certain medications and supplements.
- Luminescence: Historically used in luminous paints and watches.
| Property | Calcium Sulfide |
|---|---|
| Bond Type | Ionic |
| Melting Point | 2500°C |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in water |

Checklist: Identifying Ionic vs. Covalent Compounds
- Check Electronegativity: A difference >1.7 suggests ionic bonding.
- Observe Physical State: Solids at room temperature often indicate ionic compounds.
- Test Conductivity: Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten or aqueous states.
Final Thoughts

Calcium sulfide is unequivocally an ionic compound, characterized by its high melting point, conductivity, and crystal structure. Its unique properties make it valuable in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and beyond. Understanding its bonding type not only satisfies scientific curiosity but also aids in its practical applications.
Is calcium sulfide soluble in water?
+Calcium sulfide is slightly soluble in water and decomposes in acids.
What are the uses of calcium sulfide?
+It is used in fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and historically in luminous paints.
How can you identify an ionic compound?
+Look for high melting points, conductivity in molten or aqueous states, and a crystal lattice structure.
Related Keywords: ionic compounds, covalent compounds, chemical bonding, calcium sulfide properties, calcium sulfide uses, chemical classification, electronegativity difference, crystal lattice structure, agricultural applications, pharmaceutical uses.