Cell Nucleus Analogy: Unlocking the Brain of the Cell

The cell nucleus is often likened to the brain of the cell, and for good reason. It houses the cell’s DNA, controls gene expression, and orchestrates cellular activities. Understanding the cell nucleus analogy not only sheds light on its critical role but also simplifies complex biological concepts. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or simply curious about cellular biology, this guide breaks down the nucleus’s functions and significance in an easy-to-understand manner.
What is the Cell Nucleus?

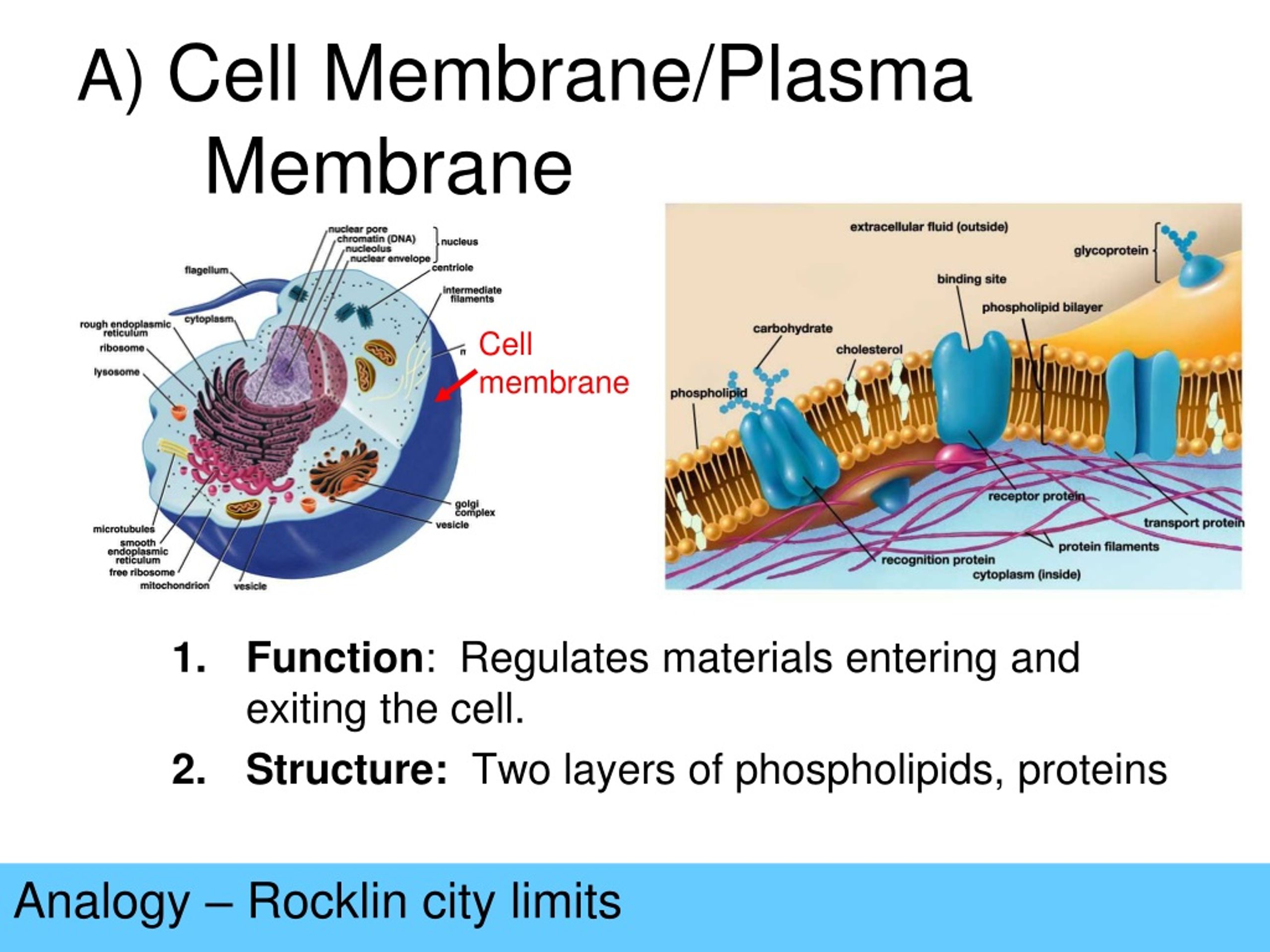
The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains the cell’s genetic material, DNA, organized into chromosomes. Acting as the cell’s command center, the nucleus regulates growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Without it, the cell would lack direction and functionality.
📌 Note: Prokaryotic cells, like bacteria, lack a nucleus. Their genetic material floats freely in the cytoplasm.
The Cell Nucleus Analogy: Why the Brain Comparison?

Comparing the cell nucleus to the brain highlights its central role in decision-making and control. Just as the brain directs bodily functions, the nucleus governs cellular processes. Here’s how the analogy holds up:
- DNA as the Instruction Manual: The nucleus stores DNA, which contains instructions for protein synthesis and cell function, much like the brain stores memories and knowledge.
- Gene Expression as Decision-Making: The nucleus decides which genes to activate or suppress, similar to how the brain makes decisions based on available information.
- Nuclear Envelope as Protection: The nuclear envelope safeguards DNA, akin to the skull protecting the brain.
Key Functions of the Cell Nucleus

The nucleus performs several vital functions, ensuring the cell’s survival and proper functioning.
1. Genetic Information Storage
The nucleus houses DNA, the blueprint of life. This genetic material is passed on during cell division, ensuring continuity and diversity.
2. Protein Synthesis Regulation
The nucleus controls which proteins are synthesized by transcribing DNA into RNA. This RNA is then transported to the cytoplasm for protein assembly.
3. Cell Cycle Control
The nucleus regulates the cell cycle, ensuring accurate DNA replication and division. Errors in this process can lead to diseases like cancer.
| Function | Analogous Brain Function |
|---|---|
| DNA Storage | Memory Storage |
| Gene Expression | Decision-Making |
| Cell Cycle Control | Bodily Function Regulation |

Practical Applications of Understanding the Cell Nucleus
Grasping the cell nucleus analogy has real-world implications, particularly in medicine and biotechnology.
- Cancer Research: Understanding nuclear function helps identify abnormalities in cell division, aiding cancer treatment.
- Gene Therapy: Targeting the nucleus allows for the correction of genetic disorders.
- Stem Cell Research: Knowledge of nuclear control is crucial for developing stem cell therapies.
Checklist: Key Takeaways About the Cell Nucleus
- The nucleus is the cell’s control center, akin to the brain.
- It stores DNA, regulates gene expression, and controls the cell cycle.
- The nuclear envelope protects genetic material.
- Understanding the nucleus is vital for advancements in medicine and biotechnology.
What is the main function of the cell nucleus?
+The cell nucleus primarily stores DNA, regulates gene expression, and controls the cell cycle.
Why is the cell nucleus compared to the brain?
+The nucleus acts as the cell’s control center, directing functions much like the brain directs bodily activities.
Can cells survive without a nucleus?
+Eukaryotic cells cannot survive long without a nucleus, as it is essential for DNA storage and gene regulation. Prokaryotic cells, however, lack a nucleus and function differently.
In summary, the cell nucleus analogy as the brain of the cell simplifies its complex role. By storing DNA, regulating genes, and controlling cellular processes, the nucleus ensures the cell’s survival and function. Whether for academic curiosity or practical applications, understanding the nucleus unlocks insights into the very building blocks of life.
cell nucleus function, cell nucleus structure, eukaryotic cell, DNA storage, gene expression, cell cycle control



