Cell Wall Picture: A Visual Guide to Plant Structure
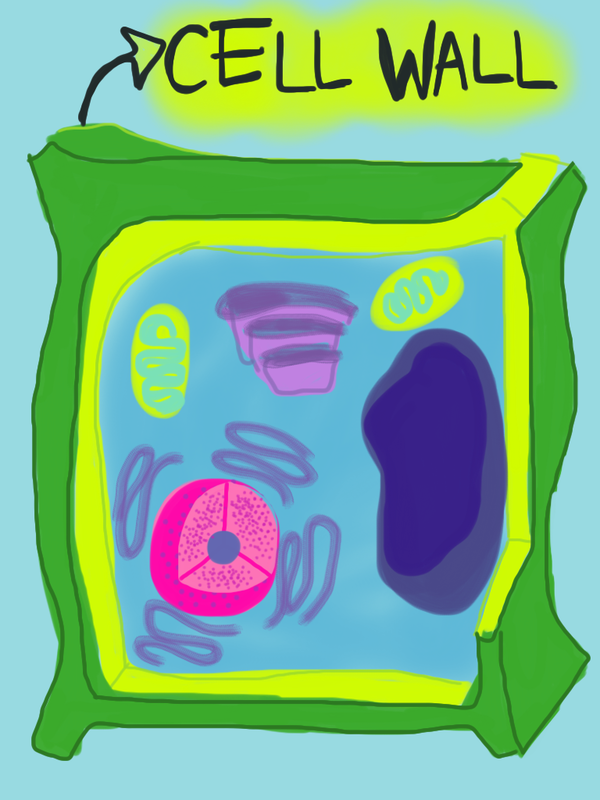

Understanding the cell wall structure of plants is essential for anyone interested in botany, agriculture, or plant biology. A cell wall picture provides a visual guide that simplifies complex plant anatomy, making it easier to grasp how plants maintain their shape, protect themselves, and grow. Whether you're a student, researcher, or gardening enthusiast, this guide will help you explore the intricate details of plant cells, focusing on the cell wall’s role and composition. From its primary functions to its layered structure, this post breaks down everything you need to know in an easy-to-follow format, complete with checklists and FAQs for quick reference. (plant cell structure, cell wall function, plant anatomy)
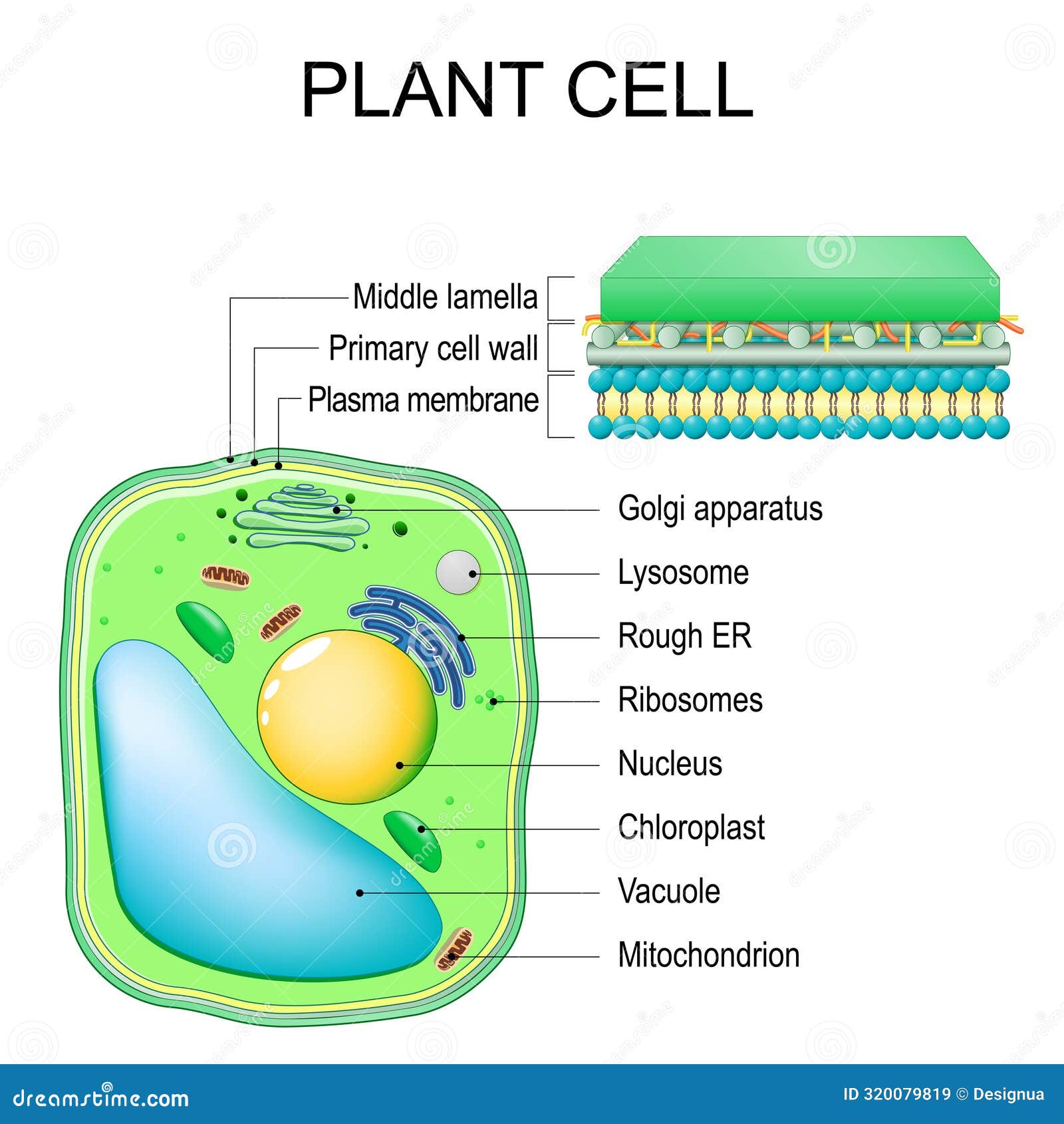
What is the Plant Cell Wall?

The plant cell wall is a rigid layer located outside the cell membrane, providing structural support and protection. Unlike animal cells, plant cells rely on this wall to maintain their shape and withstand external pressures. It is primarily composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, which work together to form a strong yet flexible barrier. The cell wall also plays a crucial role in cell growth, communication, and defense against pathogens. (cellulose structure, plant cell components, cell wall composition)
Layers of the Plant Cell Wall

The plant cell wall consists of three main layers: the primary cell wall, the secondary cell wall, and in some cases, the middle lamella. Each layer has distinct functions and compositions:
- Primary Cell Wall: Thin, flexible, and allows cell expansion during growth.
- Secondary Cell Wall: Thicker and provides additional strength, often found in mature cells.
- Middle Lamella: A pectin-rich layer that acts as glue, holding adjacent cells together.
📌 Note: The primary cell wall is present in all plant cells, while the secondary cell wall forms only in specific cell types like xylem. (primary vs secondary cell wall, middle lamella function)
Functions of the Plant Cell Wall

The cell wall serves multiple critical functions in plant life, including:
- Structural Support: Maintains cell shape and prevents bursting under turgor pressure.
- Protection: Shields the cell from mechanical injury and pathogens.
- Growth Regulation: Controls cell expansion during plant development.
- Intercellular Communication: Facilitates signaling between cells.
These functions are vital for the plant’s survival and adaptability in various environments. (turgor pressure, plant defense mechanisms)
Visualizing the Cell Wall: Tools and Techniques
To study the cell wall structure, scientists use advanced imaging techniques such as:
- Light Microscopy: Provides basic visualization of cell walls stained with dyes like calcofluor white.
- Electron Microscopy: Offers high-resolution images to observe fine details of cell wall layers.
- Confocal Microscopy: Allows 3D imaging of cell walls in living tissues.
These tools help researchers understand the cell wall’s complexity and its role in plant physiology. (microscopy techniques, cell wall imaging)
Checklist for Studying Plant Cell Walls

Use this checklist to ensure you cover all key aspects when studying plant cell walls:
- Identify the main components: cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin.
- Understand the differences between primary and secondary cell walls.
- Learn the functions of the middle lamella.
- Explore imaging techniques for visualizing cell walls.
- Relate cell wall structure to plant growth and defense mechanisms.
(cell wall components, plant growth stages)
In summary, the plant cell wall is a fascinating and essential structure that supports plant life. By understanding its composition, layers, and functions, you can gain deeper insights into plant biology. Whether you're studying for academic purposes or applying this knowledge in agriculture, visualizing the cell wall through pictures and diagrams is a powerful learning tool. Use the provided checklist and FAQs to reinforce your understanding and explore related topics further. (plant biology, agricultural science)
What is the main component of the plant cell wall?
+
The primary component of the plant cell wall is cellulose, which provides rigidity and strength. (cellulose function)
How does the cell wall differ from the cell membrane?
+
The cell wall is a rigid, external structure made of cellulose, while the cell membrane is a flexible, selective barrier composed of lipids and proteins. (cell membrane vs cell wall)
Why is the secondary cell wall important?
+
The secondary cell wall provides additional strength and support, particularly in mature cells like those in wood or fibers. (secondary cell wall function)



