Is Condensation Exothermic or Endothermic? Uncover the Truth!

Have you ever wondered whether condensation is an exothermic or endothermic process? This question often arises in chemistry, physics, and even in everyday life. Understanding the nature of condensation can help clarify how energy is transferred during phase changes. In this post, we’ll explore the science behind condensation, its energy dynamics, and why it matters. Whether you’re a student, a curious learner, or someone looking for practical insights, this guide will shed light on the truth about condensation, (phase changes, heat transfer, thermodynamics).
What is Condensation?

Condensation is the process by which a substance changes from its gaseous state to a liquid state. This occurs when gas molecules lose energy, slow down, and come closer together. Everyday examples include water vapor turning into dew on grass or fog forming in the air. Condensation plays a crucial role in the water cycle, weather patterns, and industrial applications, (water cycle, dew point, industrial processes).
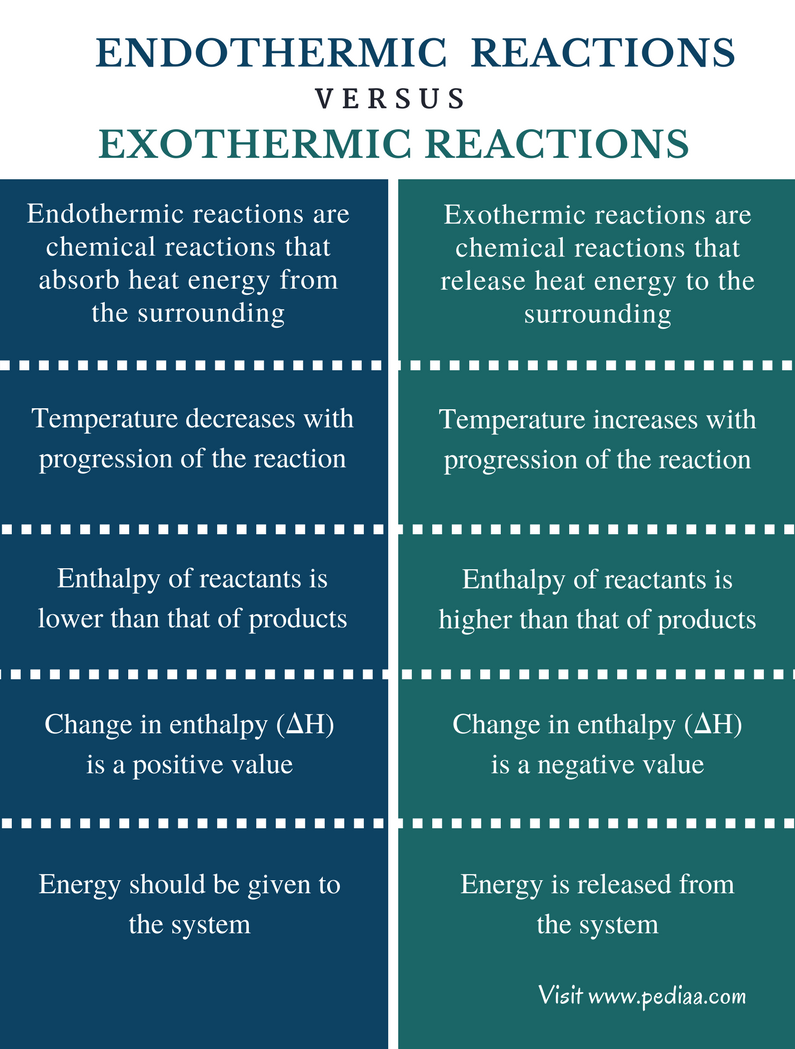
Exothermic vs. Endothermic Processes

To determine whether condensation is exothermic or endothermic, we need to understand these terms:
- Exothermic: A process that releases energy, usually in the form of heat, to its surroundings.
- Endothermic: A process that absorbs energy from its surroundings.
Knowing which category condensation falls into helps us grasp its impact on energy systems, (energy release, heat absorption, thermodynamics).
Is Condensation Exothermic or Endothermic?
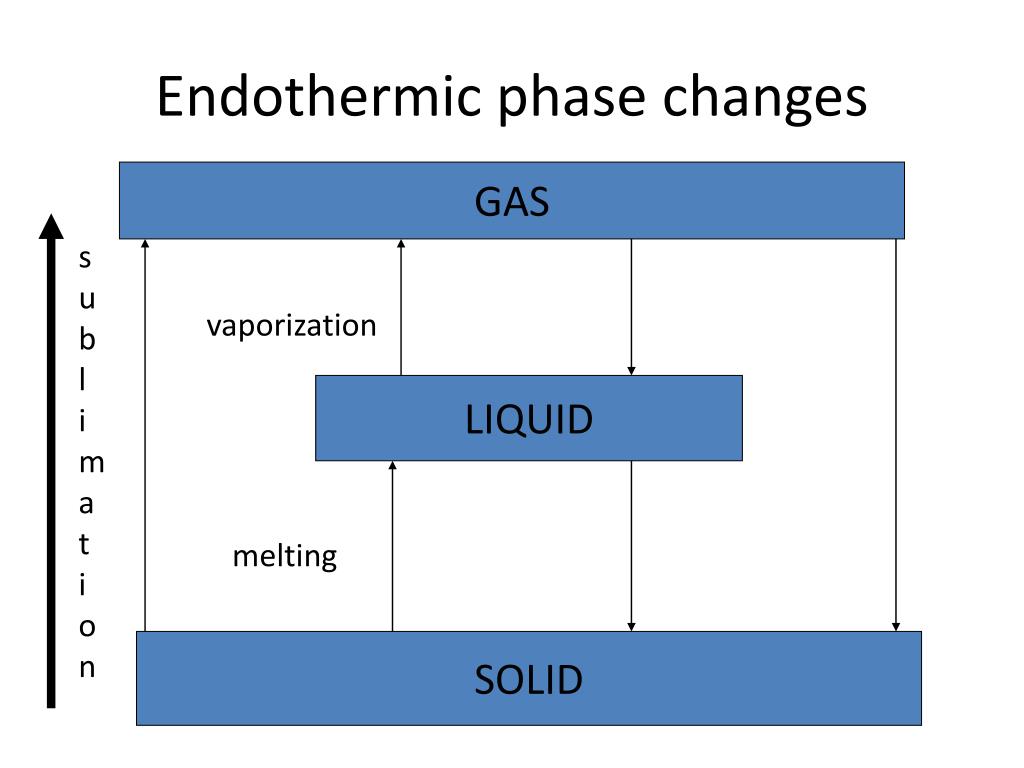
Condensation is an exothermic process. As gas molecules transition to a liquid state, they release energy in the form of heat. This is why you might feel warmth when water vapor condenses on your skin or on cold surfaces. The energy released during condensation is a result of the molecules forming stronger intermolecular forces in the liquid state, (exothermic reaction, intermolecular forces, heat release).
Why Does Condensation Release Heat?
During condensation, gas molecules slow down and come closer together, forming a liquid. This process involves the formation of stronger bonds between molecules, which releases the excess energy as heat. For example, when water vapor condenses into liquid water, the heat released can be observed in phenomena like steam warming surfaces it touches, (molecular bonds, heat energy, steam condensation).
Practical Applications of Condensation

Understanding condensation’s exothermic nature is vital in various fields:
- Weather and Climate: Condensation drives cloud formation and precipitation, influencing weather patterns.
- Industrial Processes: It’s used in distillation, power generation, and refrigeration systems.
- Everyday Life: Examples include dehumidifiers, air conditioners, and even the formation of morning dew, (cloud formation, distillation, dehumidifiers).
Key Takeaways Checklist
- Condensation is the process of gas turning into liquid.
- It is an exothermic process that releases heat.
- This heat release occurs due to the formation of stronger molecular bonds.
- Condensation has practical applications in weather, industry, and daily life.
💡 Note: While condensation is exothermic, the reverse process, evaporation, is endothermic as it absorbs heat from the surroundings.
Condensation is undeniably an exothermic process, releasing heat as gas molecules transform into a liquid state. This understanding is not only fundamental in science but also has practical implications in various fields. By grasping the basics of condensation, you can better appreciate its role in both natural phenomena and technological applications. Whether you’re studying thermodynamics or simply curious about how the world works, knowing the truth about condensation is a valuable piece of knowledge, (thermodynamics, natural phenomena, technological applications).
What is condensation in simple terms?
+
Condensation is the process where a gas changes into a liquid, such as water vapor turning into dew.
Why is condensation exothermic?
+
Condensation is exothermic because it releases heat as gas molecules form stronger bonds in the liquid state.
How does condensation affect weather?
+
Condensation is key to cloud formation and precipitation, driving weather patterns like rain and snow.



