Essential Medication Dosage Conversion Chart: Quick Guide
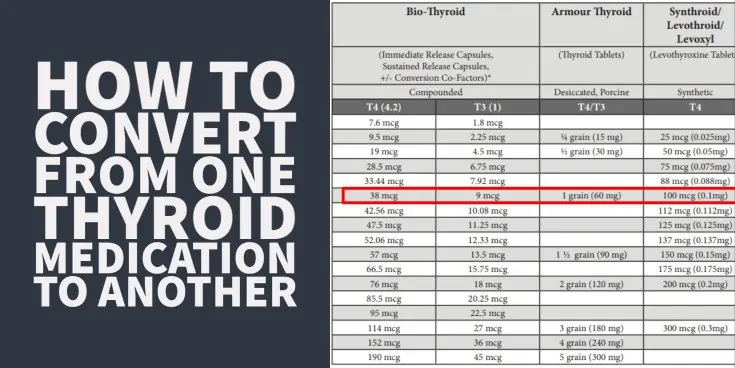
Navigating Medication Dosage Conversions: A Quick and Essential Guide
Medication dosage conversions can be a daunting task, especially when dealing with different units of measurement. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, caregiver, or patient, understanding how to accurately convert dosages is crucial for safe and effective treatment. This guide provides a medication dosage conversion chart and step-by-step instructions to simplify the process, ensuring you administer the correct amount every time. (medication dosage conversion, dosage calculator, drug dosage chart)
Why Medication Dosage Conversion Matters
Administering the wrong dosage can lead to serious health risks, including overdose or under-treatment. Medications often come in various forms (tablets, liquids, injections) and units (mg, mcg, mL), making conversions essential. This guide focuses on common dosage conversions and provides a handy chart for quick reference. (medication safety, dosage errors, pharmaceutical calculations)
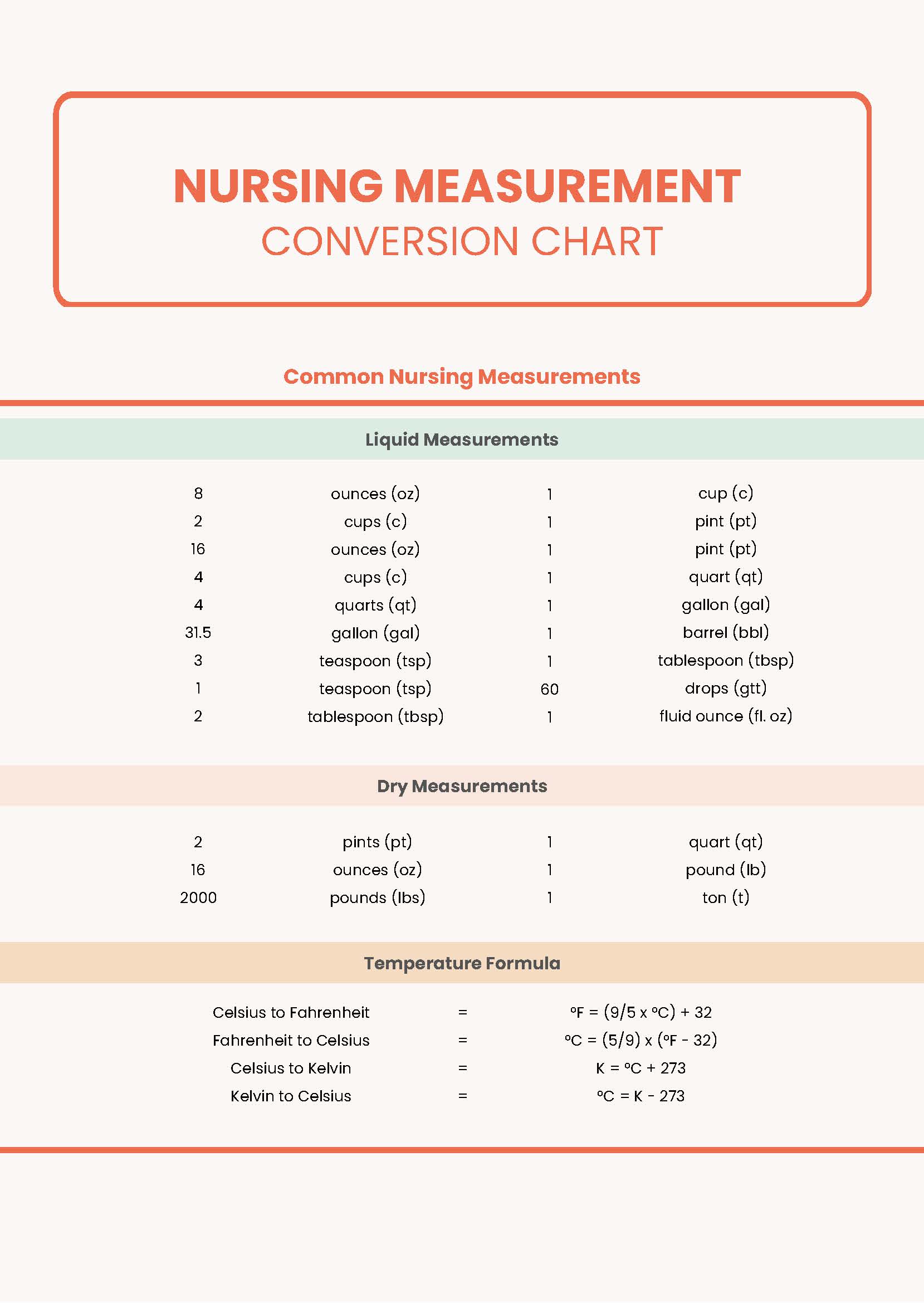
Common Dosage Units and Conversions

Understanding the basic units of measurement is the first step in mastering dosage conversions. Here are the most common units:
- Milligrams (mg): Used for solid medications like tablets or capsules.
- Micrograms (mcg): Common for high-potency drugs like vitamins or hormones.
- Milliliters (mL): Used for liquid medications such as syrups or suspensions.
Below is a dosage conversion chart to help you navigate these units:
| From Unit | To Unit | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| mg | mcg | 1 mg = 1,000 mcg |
| mcg | mg | 1 mcg = 0.001 mg |
| mg | mL | Depends on drug concentration (check label) |
💡 Note: Always verify the concentration of liquid medications, as it varies by product.
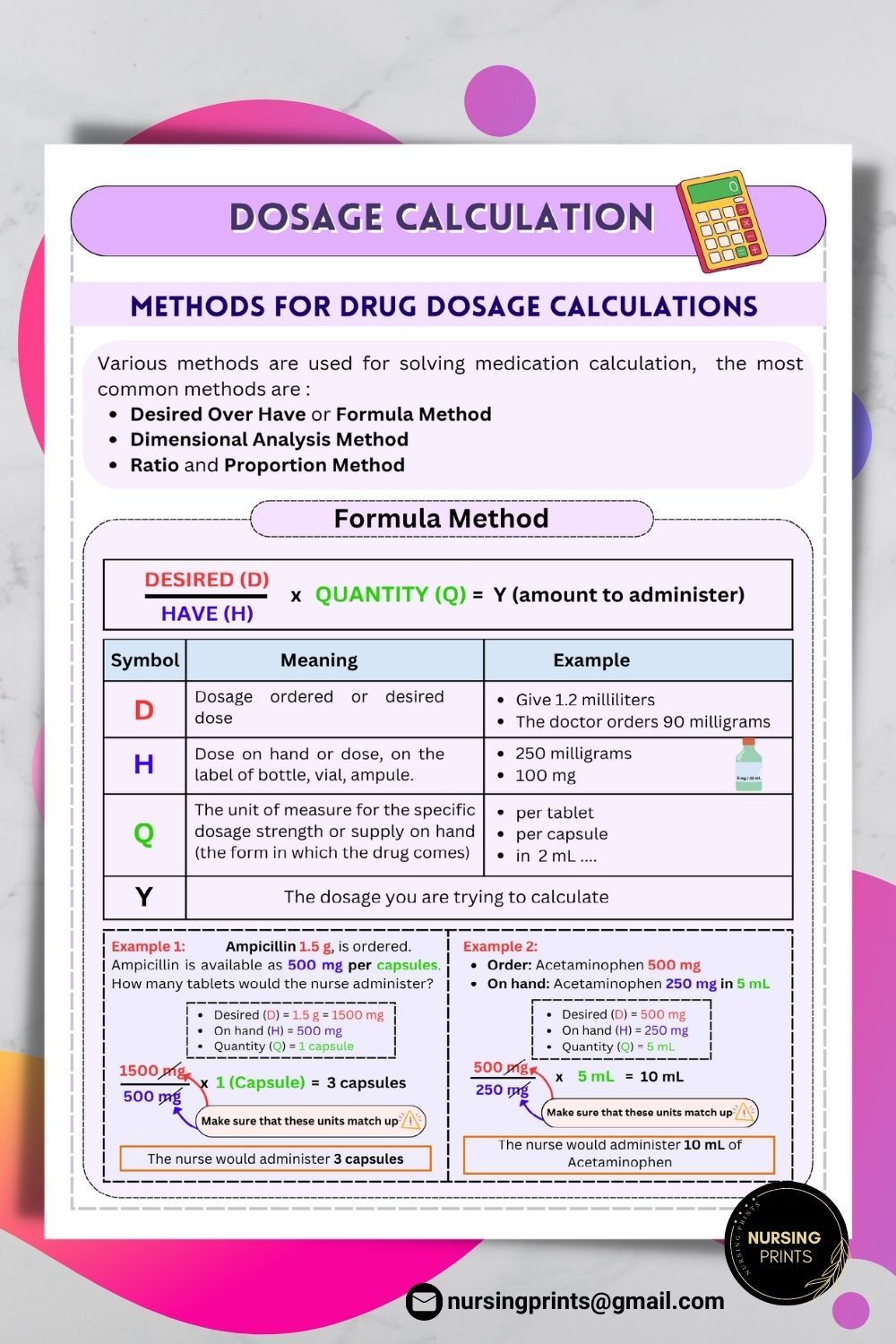
Step-by-Step Dosage Conversion Guide
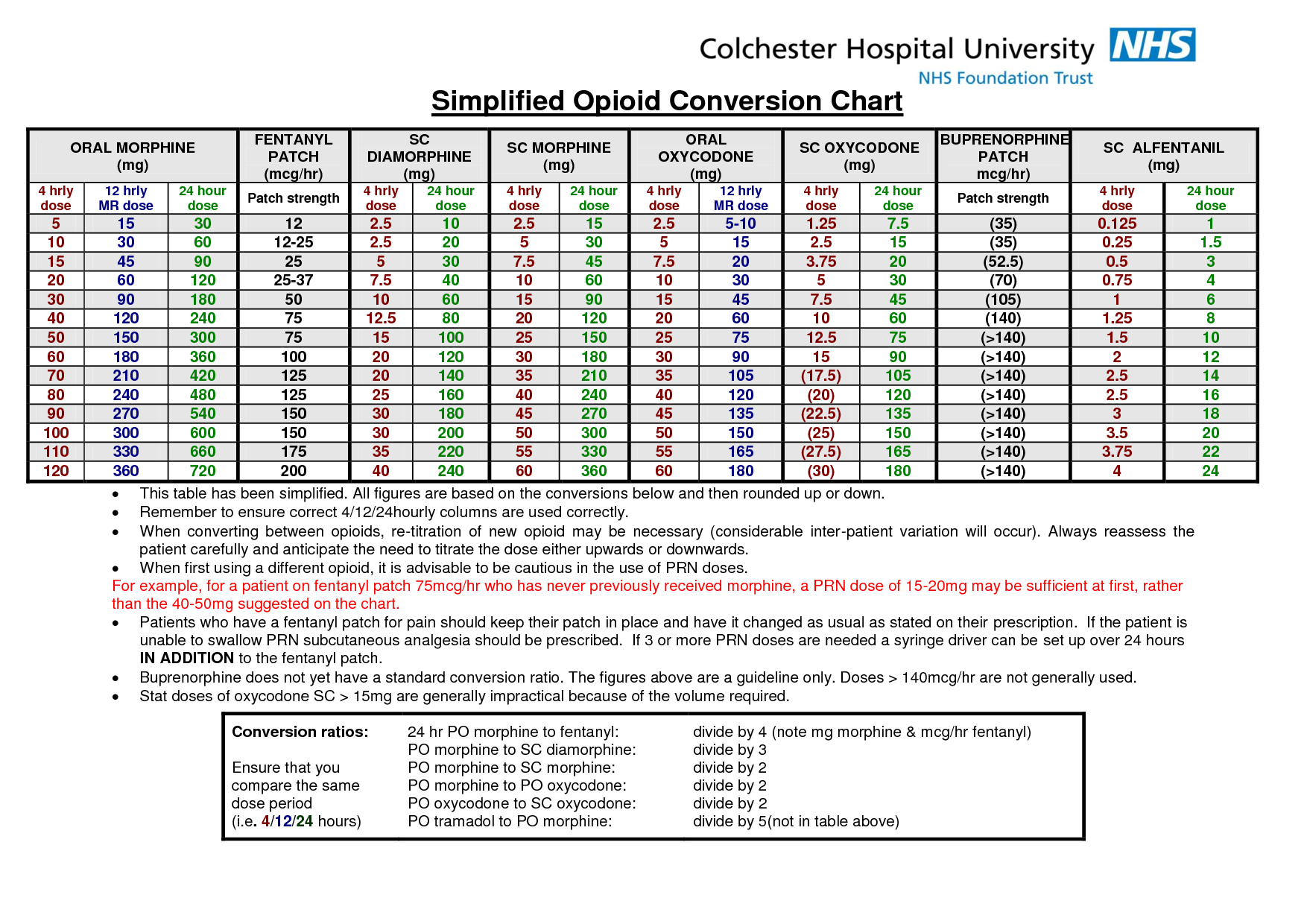
Converting dosages doesn’t have to be complicated. Follow these steps for accurate results:
- Identify the Current Dosage: Determine the current unit (e.g., mg, mcg) and amount.
- Find the Conversion Factor: Use the chart above or a dosage calculator for precise conversions.
- Perform the Calculation: Multiply or divide the dosage by the conversion factor.
- Double-Check Your Work: Ensure the final dosage aligns with the prescribed amount.
Example Conversion
Convert 5 mg to mcg:
5 mg × 1,000 = 5,000 mcg
⚠️ Note: Always consult a healthcare professional if unsure about a dosage.
Tools to Simplify Dosage Conversions
For those who prefer digital assistance, dosage calculator apps and online tools can streamline the process. These tools are especially useful for complex conversions or when dealing with multiple medications. (dosage calculator app, pharmaceutical tools, medication management)
Key Takeaways: Dosage Conversion Checklist
- Understand Units: Familiarize yourself with mg, mcg, and mL.
- Use a Chart: Refer to a medication dosage conversion chart for quick reference.
- Verify Concentrations: Always check the label for liquid medication concentrations.
- Double-Check Calculations: Accuracy is critical in medication dosages.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult a healthcare provider for complex conversions.
By mastering dosage conversions, you ensure safe and effective medication administration. Whether you’re using a chart or a dosage calculator, precision is key. (medication safety, dosage accuracy, healthcare tips)
What is the most common dosage unit for solid medications?
+Milligrams (mg) are the most common unit for solid medications like tablets or capsules.
How do I convert mg to mcg?
+Multiply the mg value by 1,000 to convert it to mcg (e.g., 5 mg = 5,000 mcg).
Can I use a dosage calculator for all medications?
+Yes, dosage calculators are useful for most medications, but always verify results with a healthcare professional.
Understanding medication dosage conversions is essential for anyone involved in administering medications. With the right tools and knowledge, you can ensure accuracy and safety in every dose. Whether you rely on a dosage conversion chart or digital tools, always prioritize precision and consult professionals when in doubt. (medication safety, dosage accuracy, healthcare tips)


