Disruptive vs. Stabilizing Selection: Evolution's Tug-of-War Explained
Evolution is a complex and fascinating process, driven by various mechanisms that shape the diversity of life on Earth. Two key forces, disruptive selection and stabilizing selection, play a crucial role in this process, often acting as opposing forces in the natural world. Understanding these concepts is essential for grasping how species evolve and adapt to their environments.
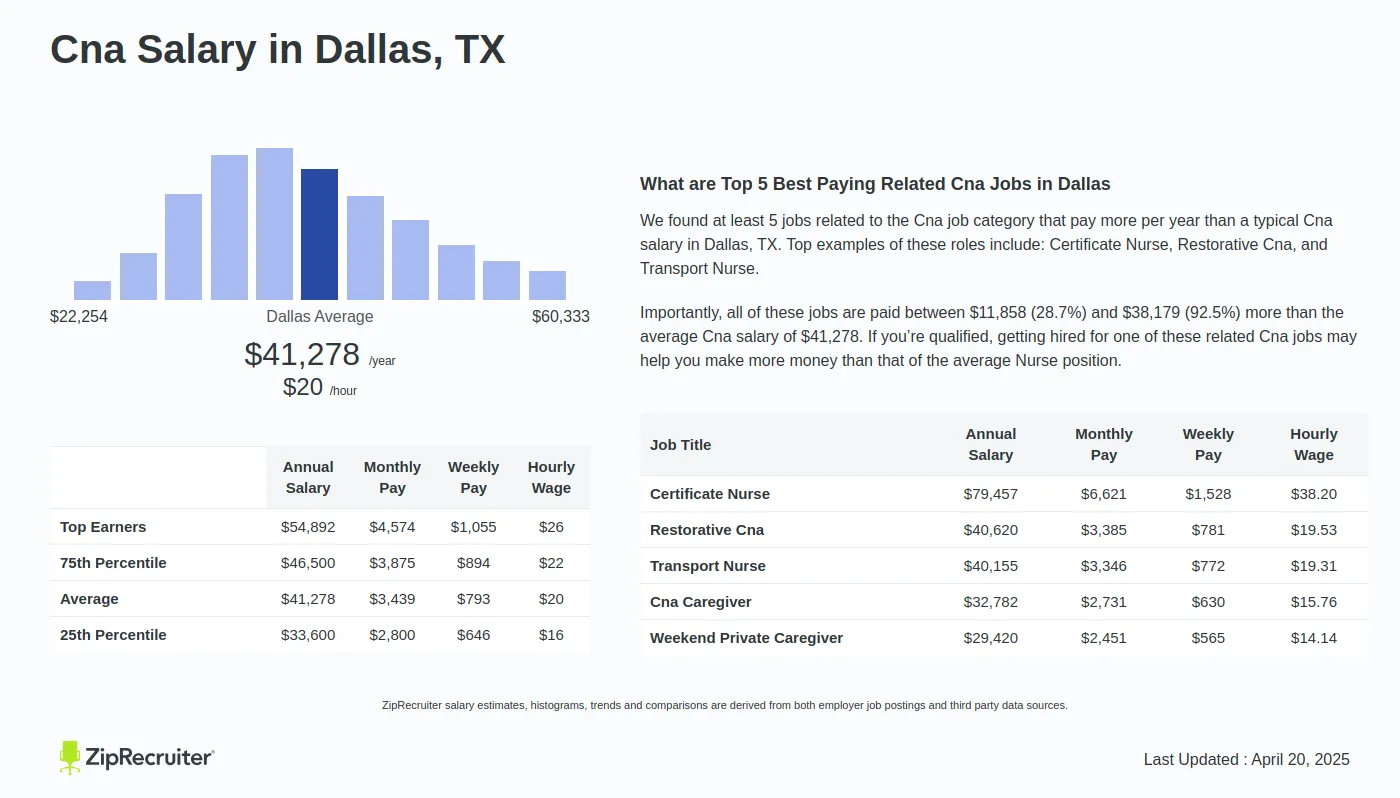
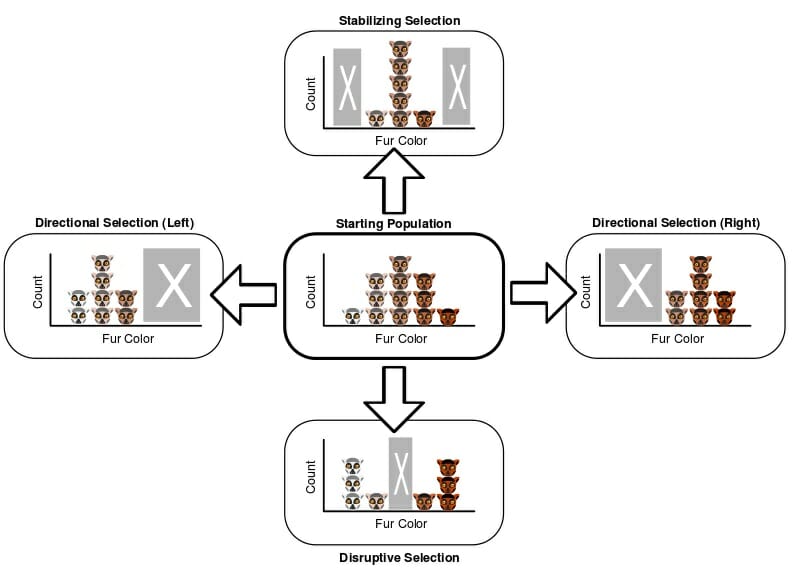
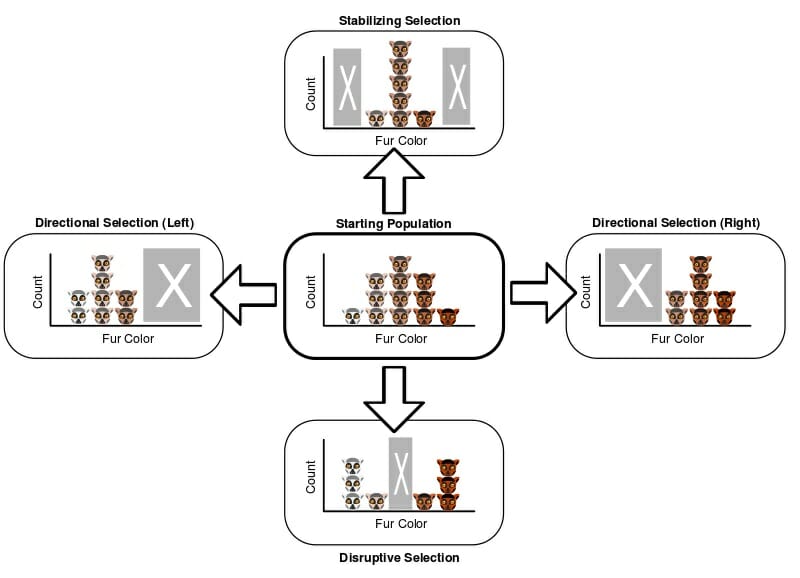
What is Disruptive Selection?

Disruptive selection occurs when individuals at both extremes of a trait range have higher fitness than those in the middle. This type of selection favors diversity by pushing a population toward two distinct phenotypes. For example, in a bird population with varying beak sizes, birds with very small or very large beaks might thrive better than those with medium-sized beaks.
📌 Note: Disruptive selection can lead to speciation over time as populations diverge into distinct groups.
What is Stabilizing Selection?

In contrast, stabilizing selection favors the average phenotype, reducing extreme variations within a population. This mechanism maintains the status quo by selecting against individuals with extreme traits. For instance, in a population of rabbits, those with moderate fur thickness are more likely to survive, while those with too thin or too thick fur are at a disadvantage.
📌 Note: Stabilizing selection is common in stable environments where extreme traits are less advantageous.
Key Differences Between Disruptive and Stabilizing Selection

To better understand these concepts, let’s compare them in a table:
| Aspect | Disruptive Selection | Stabilizing Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Effect on Diversity | Increases diversity | Reduces diversity |
| Favored Traits | Extreme traits | Average traits |
| Outcome | Potential speciation | Maintains population stability |

Real-World Examples of Selection in Action
- Disruptive Selection: In a population of insects, some may evolve to feed on different plants, leading to distinct groups with specialized traits.
- Stabilizing Selection: Human birth weight is a classic example, where babies of average weight have higher survival rates compared to those born underweight or overweight.
How Selection Shapes Evolution

Both disruptive and stabilizing selection are integral to evolutionary biology. They highlight the dynamic nature of natural selection, where environmental pressures can either promote diversity or maintain uniformity. Understanding these mechanisms helps us predict how species might respond to changing environments, such as climate change or habitat loss.
Checklist: Key Takeaways
- Disruptive Selection: Favors extreme traits, increases diversity, and can lead to speciation.
- Stabilizing Selection: Favors average traits, reduces diversity, and maintains population stability.
- Real-World Applications: Observed in insect specialization, human birth weight, and more.
What is the main difference between disruptive and stabilizing selection?
+Disruptive selection favors extreme traits and increases diversity, while stabilizing selection favors average traits and reduces diversity.
Can disruptive selection lead to the formation of new species?
+Yes, disruptive selection can lead to speciation as populations diverge into distinct groups with specialized traits.
Why is stabilizing selection important in stable environments?
+Stabilizing selection maintains population stability by selecting against extreme traits that are less advantageous in consistent environments.
In summary, disruptive and stabilizing selection are two sides of the evolutionary coin, each playing a vital role in shaping life’s diversity. While disruptive selection drives change and innovation, stabilizing selection ensures survival through consistency. Together, they illustrate the delicate balance of evolution’s tug-of-war, highlighting the adaptability and resilience of life on Earth. (evolutionary biology, natural selection, genetic diversity)