Unveiling the Eye: A Detailed Dissection Guide

The human eye, a marvel of biological engineering, has captivated scientists, artists, and curious minds for centuries. Whether you're a medical student, a biology enthusiast, or simply intrigued by the intricacies of anatomy, understanding the structure of the eye is both fascinating and educational. This guide, "Unveiling the Eye: A Detailed Dissection Guide," walks you through the process of dissecting an eye, revealing its layers, functions, and significance. From the cornea to the retina, we’ll explore each component step by step, ensuring clarity and precision. Perfect for educational purposes or personal exploration, this guide is your gateway to mastering eye anatomy, (eye dissection guide, eye anatomy tutorial, human eye structure)
Understanding the Basics of Eye Anatomy

Before diving into the dissection process, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental structure of the eye. The eye is composed of three main layers: the outer layer (cornea and sclera), the middle layer (iris, choroid, and ciliary body), and the inner layer (retina). Each layer plays a unique role in vision and overall eye function. Familiarizing yourself with these components will make the dissection process smoother and more insightful, (eye layers, vision anatomy, ocular structure)
Tools and Materials Needed for Eye Dissection

To successfully dissect an eye, you’ll need the following tools and materials:
- Fresh or preserved eye specimen (bovine or sheep eyes are commonly used)
- Dissection tray
- Scalpel or surgical blade
- Forceps
- Scissors
- Probe
- Gloves and goggles for safety
- Disinfectant solution
Ensure all tools are sterilized before use to maintain a safe and hygienic environment, (dissection tools, eye specimen preparation, anatomical dissection kit)
Step-by-Step Eye Dissection Guide

Step 1 – Preparing the Specimen
Begin by placing the eye specimen in the dissection tray. Rinse it gently with disinfectant solution to remove any debris. Identify the cornea (clear front portion) and the sclera (white outer layer). This initial observation sets the stage for the dissection, (eye specimen preparation, cornea identification, sclera anatomy)
Step 2 – Making the Initial Incision
Using a scalpel, make a careful circular incision around the cornea. This will allow you to lift the outer layer and expose the underlying structures. Be precise to avoid damaging the delicate tissues, (initial incision technique, corneal dissection, surgical precision)
Step 3 – Exploring the Middle Layer
Once the outer layer is lifted, you’ll encounter the iris (colored part) and the lens. Use forceps to gently remove the lens, revealing the vitreous humor, a gel-like substance that fills the eye. This step provides insight into how light is focused onto the retina, (iris exploration, lens removal, vitreous humor function)
Step 4 – Examining the Retina
The final layer, the retina, is where light is converted into neural signals. Carefully peel back the choroid to observe the retina’s intricate structure. Look for the optic nerve, which transmits visual information to the brain, (retina examination, optic nerve location, visual signal processing)
📌 Note: Always handle the specimen with care to preserve its integrity and ensure accurate observations.
Key Takeaways and Checklist
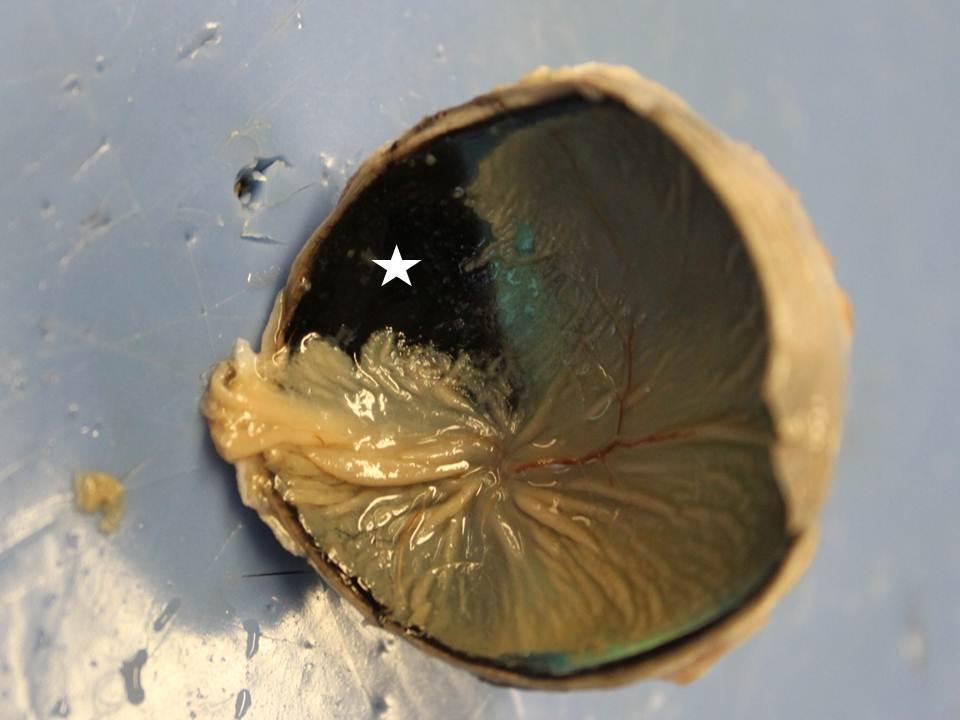
To summarize, here’s a checklist to guide your eye dissection:
- Prepare the specimen by cleaning and identifying key structures.
- Make precise incisions to expose the middle and inner layers.
- Observe the iris, lens, and vitreous humor.
- Examine the retina and optic nerve for a complete understanding.
This structured approach ensures a thorough and educational dissection experience, (eye dissection checklist, anatomical key points, dissection summary)
Dissecting the eye is not just a scientific exercise; it’s a journey into the complexities of human vision. By following this detailed guide, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for the eye’s structure and function. Whether for academic purposes or personal curiosity, this knowledge is invaluable. Remember, practice and patience are key to mastering any dissection. Happy exploring, (eye dissection tips, vision complexity, anatomical exploration)
What is the best type of eye specimen for dissection?
+Bovine or sheep eyes are commonly used due to their similarity to human eyes and availability.
Can I dissect a human eye at home?
+Dissecting a human eye at home is not recommended due to ethical and legal restrictions. Use animal specimens instead.
How do I preserve an eye specimen for dissection?
+Specimens can be preserved in a formaldehyde solution or purchased pre-preserved from educational suppliers.



