Examples of Thermal Systems: Real-World Applications Explained

Thermal systems play a crucial role in our daily lives, from heating homes to powering industries. Understanding real-world applications of these systems can help you appreciate their importance and make informed decisions. Whether you're exploring thermal energy storage, HVAC systems, or industrial heat exchangers, this guide breaks down examples of thermal systems in practical use, catering to both informational and commercial interests.
Residential Thermal Systems: Keeping Homes Comfortable

In homes, thermal systems ensure comfort through efficient heating and cooling. Here are key examples:
- HVAC Systems: Heat pumps, furnaces, and air conditioners regulate indoor temperatures.
- Radiant Floor Heating: Uses thermal energy to warm floors, providing even heat distribution.
- Water Heaters: Store and supply hot water for daily use, often powered by gas or electricity.
💡 Note: Regular maintenance of HVAC systems can improve efficiency and reduce energy costs.
For those looking to upgrade, consider energy-efficient models to save on utility bills. (energy efficiency,home improvement,thermal comfort)
Industrial Thermal Systems: Powering Manufacturing and Beyond

Industries rely on thermal systems for processes like heating, cooling, and power generation. Notable examples include:
- Heat Exchangers: Transfer heat between fluids in chemical plants and refineries.
- Boilers: Generate steam for power plants and manufacturing processes.
- Thermal Power Plants: Convert heat energy into electricity, often using coal, gas, or nuclear fuel.
| System | Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Exchangers | Chemical Processing | Efficient heat transfer |
| Boilers | Power Generation | High energy output |

Industries can invest in advanced thermal systems to enhance productivity and reduce environmental impact. (industrial efficiency,thermal technology,sustainability)
Renewable Thermal Systems: Sustainable Solutions

As the world shifts toward sustainability, renewable thermal systems are gaining traction. Key applications include:
- Solar Thermal Systems: Capture sunlight to heat water or generate electricity.
- Geothermal Heating: Utilizes Earth’s heat for residential and commercial heating.
- Thermal Energy Storage: Stores excess energy for later use, improving efficiency.
🌱 Note: Solar thermal systems can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
Explore government incentives for adopting renewable thermal solutions. (renewable energy,green technology,energy storage)
Key Takeaways: Examples of Thermal Systems
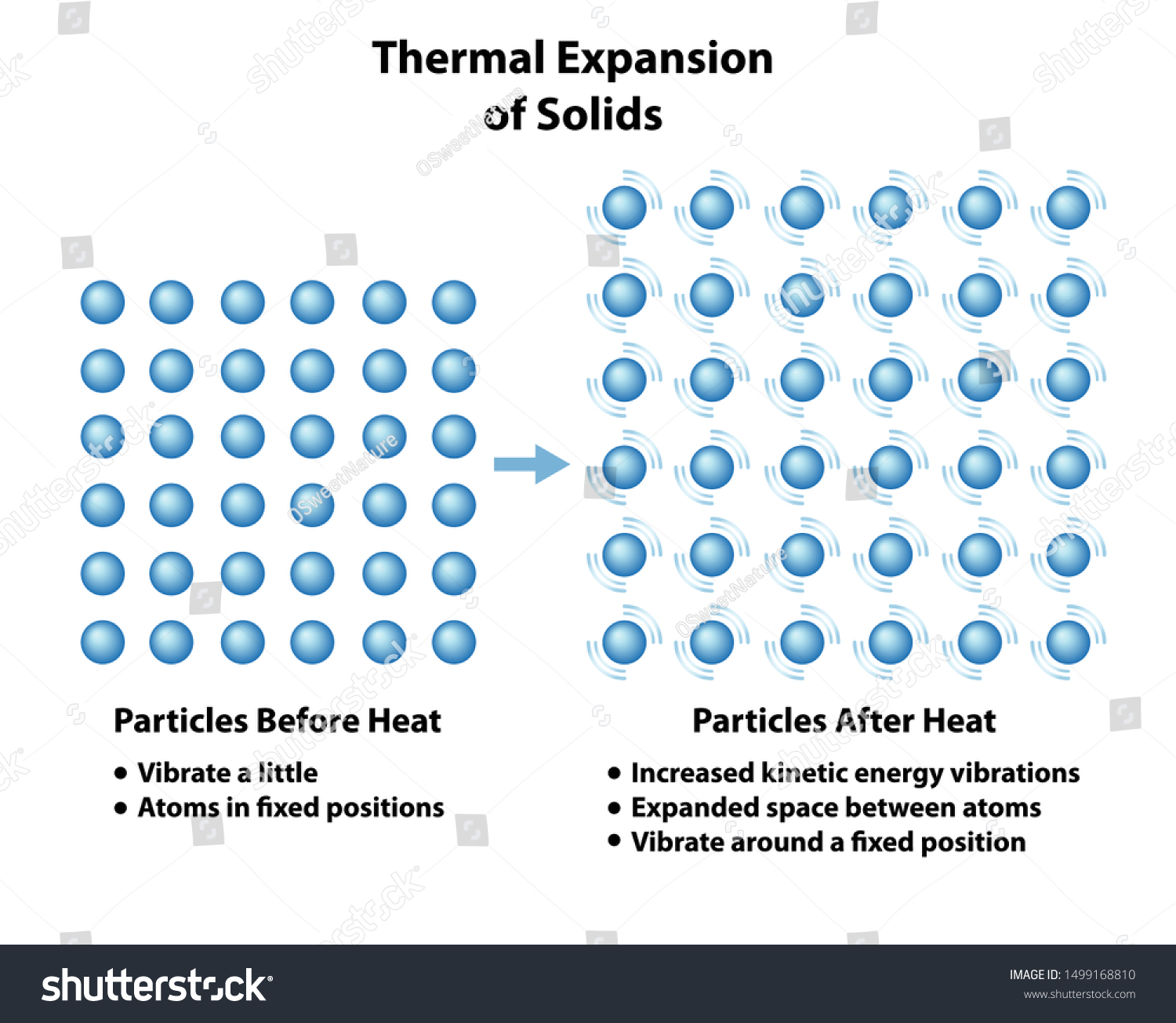
- Residential systems like HVAC and radiant heating ensure home comfort.
- Industrial systems, including boilers and heat exchangers, drive manufacturing.
- Renewable systems like solar thermal and geothermal promote sustainability.
What is the most common residential thermal system?
+HVAC systems are the most common, providing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
How do heat exchangers work in industries?
+Heat exchangers transfer heat between two fluids without mixing them, optimizing energy use.
Are solar thermal systems cost-effective?
+Yes, they reduce energy bills and qualify for government incentives in many regions.
Thermal systems are integral to modern life, from residential comfort to industrial efficiency and sustainable energy solutions. By understanding these applications, you can make informed choices tailored to your needs, whether for personal use or business growth. Explore the right thermal system today and unlock its full potential. (thermal systems,real-world applications,energy solutions)