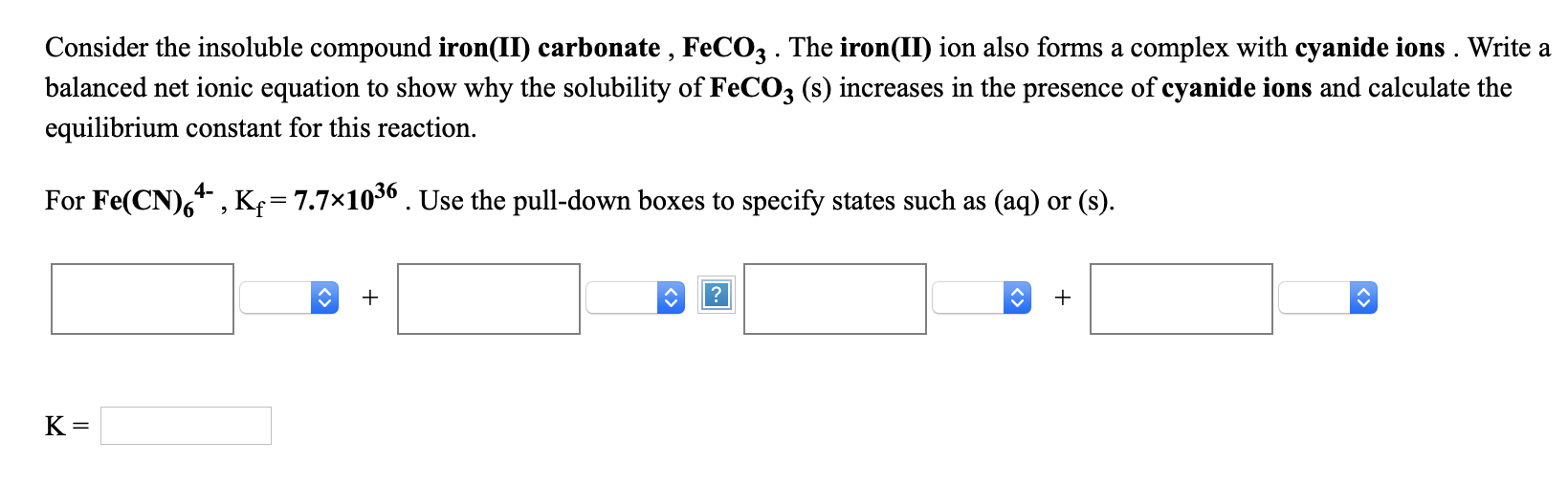
Ferrous Nitrate Formula: Quick Chemistry Guide

Ferrous nitrate, a compound with the formula Fe(NO3)2, is widely used in various industries, including agriculture, water treatment, and chemical synthesis. Understanding its formula and properties is essential for both students and professionals in chemistry. This guide provides a quick, SEO-driven overview of ferrous nitrate, its applications, and how to handle it safely. Whether you're researching for academic purposes or looking for commercial applications, this post has you covered.
What is Ferrous Nitrate? (Ferrous Nitrate Formula, Chemical Composition)

Ferrous nitrate is an inorganic compound composed of iron (Fe) and nitrate (NO3) ions. Its chemical formula, Fe(NO3)2, indicates that it contains one iron (II) ion and two nitrate ions. This compound is typically found in its hexahydrate form, Fe(NO3)2·6H2O, which includes six water molecules. Ferrous nitrate is known for its solubility in water and its use in catalytic processes, dyeing, and as a reducing agent.
How to Prepare Ferrous Nitrate (Ferrous Nitrate Synthesis, Laboratory Preparation)
Preparing ferrous nitrate in a laboratory setting involves a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Step 1: Dissolve iron (II) oxide (FeO) or iron filings in dilute nitric acid (HNO3).
- Step 2: Filter the solution to remove any undissolved particles.
- Step 3: Allow the solution to evaporate partially to crystallize the ferrous nitrate hexahydrate.
📌 Note: Always handle nitric acid with care, as it is corrosive and can cause burns.
Applications of Ferrous Nitrate (Ferrous Nitrate Uses, Industrial Applications)

Ferrous nitrate has diverse applications across industries. Some key uses include:
- Agriculture: Used as a fertilizer additive to provide iron to plants.
- Water Treatment: Acts as a coagulant to remove impurities from water.
- Chemical Synthesis: Serves as a catalyst in various chemical reactions.
- Dyeing: Employed in the textile industry for dye fixation.
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Fertilizer Additive |
| Water Treatment | Coagulant |
| Chemical Synthesis | Catalyst |
| Textile | Dye Fixation |

Safety Tips for Handling Ferrous Nitrate (Ferrous Nitrate Safety, Handling Precautions)

When working with ferrous nitrate, follow these safety precautions:
- Wear protective gloves and goggles to avoid skin and eye contact.
- Work in a well-ventilated area to prevent inhalation of fumes.
- Store in a cool, dry place away from oxidizing agents.
⚠️ Note: Ferrous nitrate is toxic if ingested. Keep out of reach of children and pets.
Quick Checklist for Ferrous Nitrate Handling (Ferrous Nitrate Guidelines, Safety Checklist)

- Understand the ferrous nitrate formula and its properties.
- Follow proper synthesis procedures for laboratory preparation.
- Use ferrous nitrate in appropriate industrial applications.
- Adhere to safety guidelines to prevent accidents.
Ferrous nitrate, with its formula Fe(NO3)2, is a versatile compound with numerous applications in chemistry and industry. By understanding its properties, preparation methods, and safety precautions, you can effectively utilize it in your work. Whether for academic research or commercial purposes, this guide ensures you have the essential knowledge to handle ferrous nitrate confidently.
What is the chemical formula of ferrous nitrate?
+
The chemical formula of ferrous nitrate is Fe(NO3)2, often found as Fe(NO3)2·6H2O in its hexahydrate form.
How is ferrous nitrate prepared in a laboratory?
+
Ferrous nitrate is prepared by dissolving iron (II) oxide or iron filings in dilute nitric acid, filtering the solution, and allowing it to crystallize.
What are the main uses of ferrous nitrate?
+
Ferrous nitrate is used in agriculture, water treatment, chemical synthesis, and textile dyeing, among other applications.



