Unlocking Functional Groups on IR Spectroscopy: A Quick Guide

Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is a powerful tool for identifying functional groups in organic compounds. Whether you're a student, researcher, or industry professional, understanding how to interpret IR spectra can significantly enhance your analytical skills. This guide will walk you through the essentials of functional groups on IR spectroscopy, helping you decode spectra with confidence. From key absorption bands to common functional groups, we’ve got you covered. (IR spectroscopy basics, functional group identification)
Understanding IR Spectroscopy: The Basics
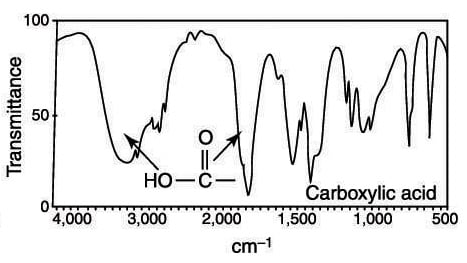
IR spectroscopy works by measuring the absorption of infrared light by a molecule. Different functional groups absorb specific wavelengths, creating unique patterns in the spectrum. These patterns are your key to identifying the presence of specific groups in a compound. (IR spectroscopy principles, molecular vibrations)
Key Regions in an IR Spectrum
- Fingerprint Region (1500–400 cm⁻¹): Provides a unique “fingerprint” for identifying compounds.
- Functional Group Region (4000–1500 cm⁻¹): Highlights specific functional groups based on their characteristic absorptions.
Identifying Common Functional Groups in IR Spectra
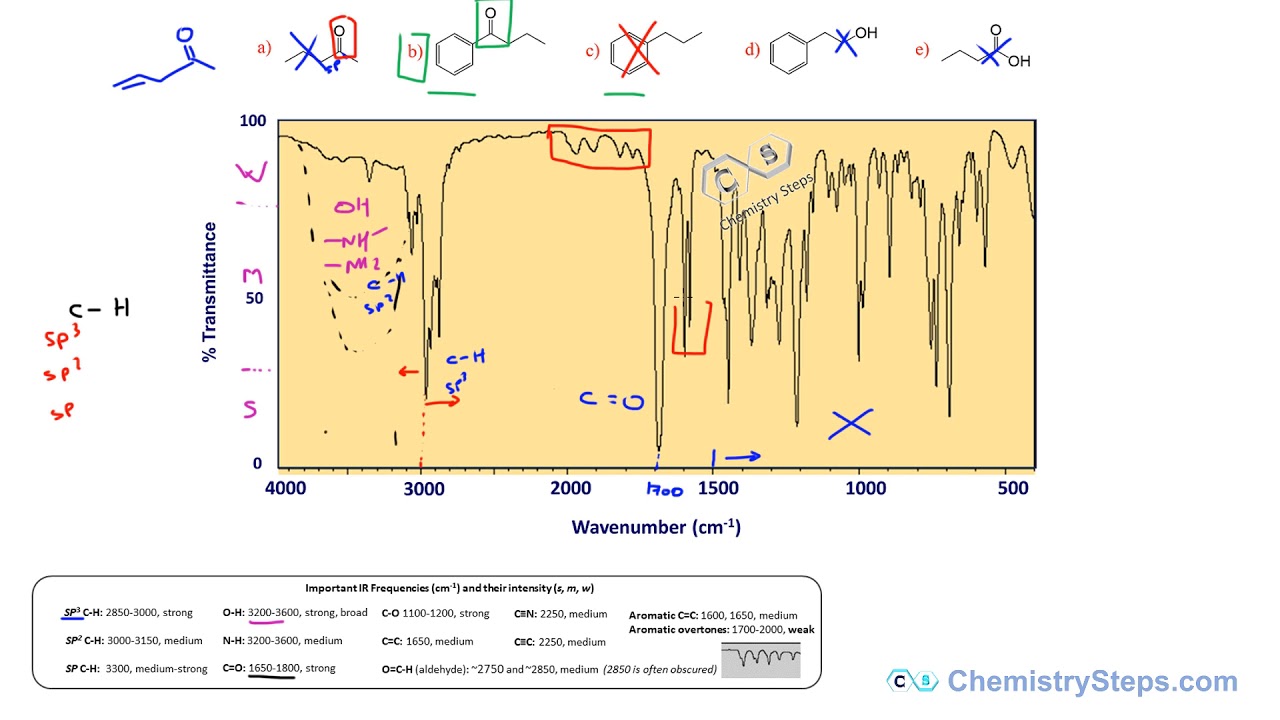
Each functional group has a distinct absorption range. Here’s a quick breakdown of the most common ones:
| Functional Group | Absorption Range (cm⁻¹) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Alkane (C-H) | 2960–2850 | Strong, sharp peaks |
| Alkene (C=C) | 1680–1620 | Medium intensity |
| Alcohol (O-H) | 3600–3200 | Broad peak |
| Carbonyl (C=O) | 1750–1700 | Strong, sharp peak |

Tips for Accurate Functional Group Identification
- Look for characteristic peaks in the functional group region.
- Compare spectra with reference libraries for confirmation.
- Consider the intensity and shape of peaks for additional clues.
📌 Note: Always ensure your IR spectrometer is properly calibrated for accurate results.
Quick Checklist for IR Spectroscopy Analysis

- Identify the fingerprint region for compound verification.
- Locate characteristic peaks in the functional group region.
- Compare with reference spectra for confirmation.
- Document your findings with clear annotations.
Mastering IR spectroscopy for functional group identification is a valuable skill in chemistry. By focusing on key absorption bands and understanding spectral patterns, you can confidently analyze organic compounds. Use this guide as a quick reference to enhance your spectroscopy skills and tackle complex analyses with ease. (IR spectroscopy analysis, organic chemistry)
What is the purpose of IR spectroscopy?
+
IR spectroscopy is used to identify functional groups in organic compounds by analyzing their absorption of infrared light.
How do I identify an alcohol group in IR spectroscopy?
+
Look for a broad peak in the range of 3600–3200 cm⁻¹, which is characteristic of the O-H stretch in alcohols.
Can IR spectroscopy identify all functional groups?
+
While IR spectroscopy is highly effective for many functional groups, some may require additional techniques like NMR for confirmation.



