HCP Atomic Packing Factor Explained: Maximizing Material Density
Understanding the HCP atomic packing factor is crucial for material scientists and engineers aiming to maximize material density. The hexagonal close-packed (HCP) structure is one of the most efficient ways atoms arrange themselves in solids, ensuring optimal space utilization. This blog explores the concept, its calculation, and practical applications, providing valuable insights for both informational and commercial audiences.
What is HCP Atomic Packing Factor?

The HCP atomic packing factor measures the efficiency of atom arrangement in a hexagonal close-packed structure. It represents the fraction of volume in a unit cell occupied by atoms. In HCP structures, atoms are packed in layers, with each atom surrounded by 12 neighbors, achieving a packing factor of approximately 74%. This high density makes HCP materials ideal for applications requiring strength and durability, such as in aerospace and automotive industries. (Atomic Packing Factor,Material Density,HCP Structure)
How to Calculate HCP Atomic Packing Factor

Step-by-Step Calculation
Calculating the HCP atomic packing factor involves the following steps:
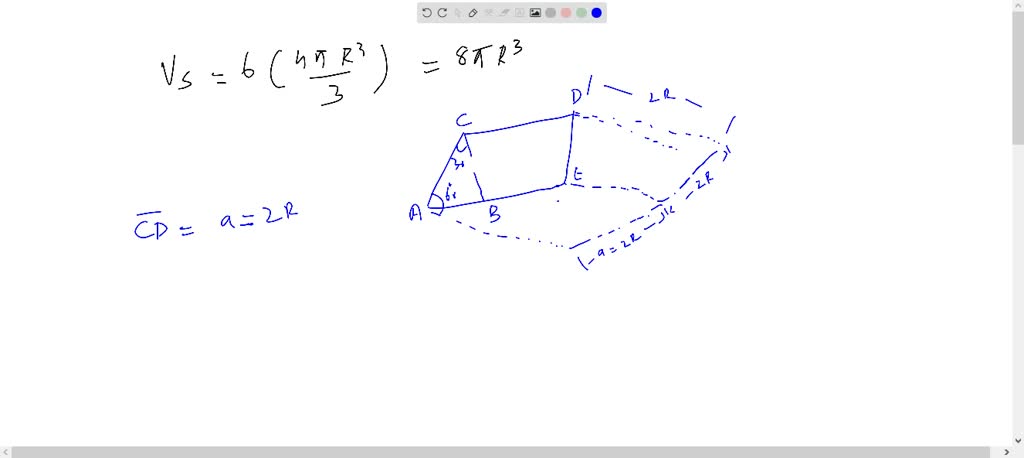
- Determine the Unit Cell Volume: Calculate the volume of the hexagonal unit cell using its dimensions.
- Calculate Atomic Volume: Find the volume of a single atom based on its radius.
- Compute Packing Factor: Divide the total atomic volume by the unit cell volume and multiply by 100 to get the percentage.
| Parameter | Formula |
|---|---|
| Unit Cell Volume | Vcell = (3√3/2) × a² × c |
| Atomic Volume | Vatom = (4/3) × π × r³ |
| Packing Factor | APF = (Number of Atoms × Vatom) / Vcell |

📌 Note: Ensure accurate measurements of atomic radius and unit cell dimensions for precise calculations.
Applications of HCP Materials

HCP materials, such as magnesium, titanium, and zinc, are widely used in industries due to their high density and strength. Their efficient atomic packing factor contributes to enhanced mechanical properties, making them suitable for:
Key Applications
- Aerospace: Lightweight yet strong components for aircraft.
- Automotive: Durable parts for vehicles, reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency.
- Biomedical: Implant materials due to their biocompatibility and strength.
The HCP atomic packing factor plays a vital role in maximizing material density, influencing the performance of various materials. By understanding its calculation and applications, professionals can optimize material selection for specific industries. Whether for informational or commercial purposes, mastering this concept is essential for advancements in material science. (Material Science,Atomic Structure,HCP Applications)
What is the HCP atomic packing factor?
+The HCP atomic packing factor is the fraction of volume in a hexagonal close-packed unit cell occupied by atoms, approximately 74%.
Why is HCP structure important in material science?
+HCP structures provide high material density and strength, making them ideal for applications in aerospace, automotive, and biomedical industries.
How do you calculate the HCP atomic packing factor?
+Calculate the unit cell volume, atomic volume, and then use the formula: APF = (Number of Atoms × Vatom) / Vcell.



