Hydrogen Cyanide Lewis Dot Structure Explained Simply

Understanding the Hydrogen Cyanide Lewis Dot Structure is crucial for anyone studying chemistry, especially in the context of molecular geometry and chemical bonding. Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN) is a highly toxic compound with significant applications in industrial processes and biological systems. By breaking down its Lewis structure, we can gain insights into its properties, reactivity, and behavior. This post will guide you through the process, ensuring you grasp the concept simply and effectively, (Hydrogen Cyanide Structure, Lewis Dot Structure, Chemical Bonding)
What is Hydrogen Cyanide?

Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN) is a colorless, highly poisonous liquid or gas with a faint almond-like odor. It consists of one hydrogen atom, one carbon atom, and one nitrogen atom. HCN plays a vital role in various industries, including plastics manufacturing and metal treatment. Its Lewis dot structure helps us understand how these atoms bond and share electrons, (Chemical Compound, Toxic Gas, Industrial Applications)
Understanding Lewis Dot Structure

The Lewis Dot Structure is a diagram that represents the valence electrons of atoms within a molecule. It uses dots to symbolize electrons and lines to indicate chemical bonds. For HCN, we need to determine the electron distribution and bonding pattern among hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen atoms. This structure is fundamental to predicting molecular shape and reactivity, (Electron Configuration, Molecular Geometry, Chemical Bonds)
Steps to Draw HCN Lewis Structure

Follow these steps to accurately draw the Hydrogen Cyanide Lewis Dot Structure:
- Step 1: Count Valence Electrons – Hydrogen has 1, Carbon has 4, and Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, totaling 10 electrons.
- Step 2: Determine Central Atom – Carbon is the central atom due to its lower electronegativity compared to Nitrogen.
- Step 3: Form Bonds – Connect Hydrogen to Carbon with a single bond and Carbon to Nitrogen with a triple bond.
- Step 4: Distribute Remaining Electrons – Place the remaining electrons as lone pairs on Nitrogen to satisfy the octet rule.
📌 Note: Ensure all atoms (except Hydrogen) have a complete octet for stability.
HCN Lewis Structure Explained

The HCN Lewis structure consists of:
- A single bond between Hydrogen and Carbon.
- A triple bond between Carbon and Nitrogen.
- Two lone pairs on the Nitrogen atom.
| Atom | Valence Electrons | Role in HCN |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | Forms single bond with Carbon |
| Carbon © | 4 | Central atom, forms bonds with H and N |
| Nitrogen (N) | 5 | Forms triple bond with Carbon, holds lone pairs |
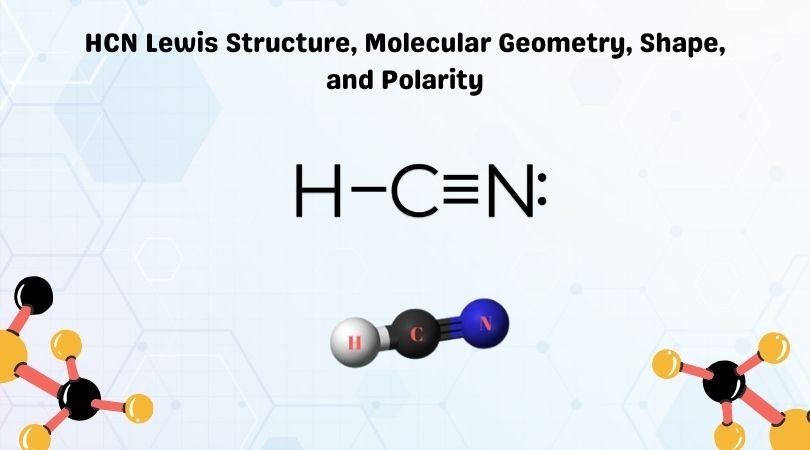
(Molecular Structure, Triple Bond, Lone Pairs)
Importance of HCN Lewis Structure

Understanding the HCN Lewis structure is essential for:
- Predicting its reactivity in chemical reactions.
- Determining its molecular geometry (linear shape).
- Explaining its polarity and solubility properties.
This knowledge is invaluable for students, researchers, and professionals in chemistry and related fields, (Chemical Reactions, Molecular Polarity, Solubility)
Mastering the Hydrogen Cyanide Lewis Dot Structure simplifies complex chemical concepts and enhances your understanding of molecular interactions. By following the steps outlined above, you can confidently draw and analyze the structure of HCN. Whether for academic purposes or professional applications, this knowledge is a valuable asset in your chemistry toolkit, (Chemical Analysis, Molecular Interactions, Chemistry Education)
What is the molecular geometry of HCN?
+HCN has a linear molecular geometry due to the arrangement of its atoms and the presence of a triple bond between Carbon and Nitrogen.
Why is Hydrogen Cyanide toxic?
+HCN inhibits cellular respiration by interfering with the electron transport chain, leading to rapid cell death and systemic toxicity.
How do you count valence electrons in HCN?
+Add the valence electrons of each atom: Hydrogen (1), Carbon (4), and Nitrogen (5), totaling 10 valence electrons.


