Lead II Iodide Molar Mass: Quick Calculation Guide

Understanding the molar mass of lead(II) iodide is crucial for anyone working in chemistry, whether you’re a student, researcher, or industry professional. Lead(II) iodide, also known as lead iodide, is a chemical compound with the formula PbI₂. Its molar mass is a fundamental property that helps in various calculations, such as stoichiometry, solution preparation, and reaction analysis. In this guide, we’ll walk you through a quick and easy calculation to determine the molar mass of lead(II) iodide, ensuring you have the knowledge to tackle any chemistry problem.
What is Lead(II) Iodide?

Lead(II) iodide is an inorganic compound composed of lead (Pb) and iodine (I). It is widely used in applications like solar cells, photography, and as a reagent in chemical synthesis. Knowing its molar mass is essential for accurate measurements and experiments.
How to Calculate the Molar Mass of PbI₂
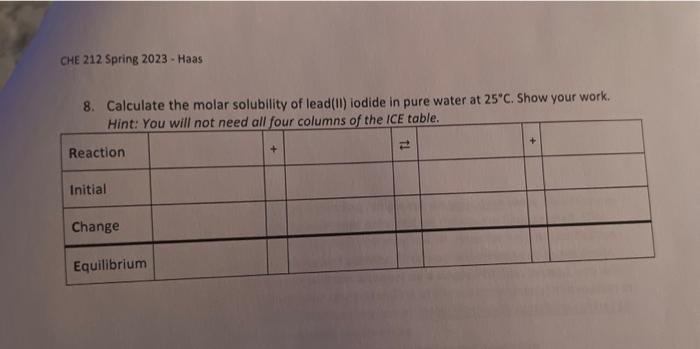
To calculate the molar mass of lead(II) iodide, follow these steps:
Identify the Atomic Masses:
- Lead (Pb): Approximately 207.2 g/mol
- Iodine (I): Approximately 126.9 g/mol
- Lead (Pb): Approximately 207.2 g/mol
Determine the Formula:
The formula for lead(II) iodide is PbI₂, indicating one lead atom and two iodine atoms.Calculate the Total Molar Mass:
[
\text{Molar Mass of PbI₂} = (\text{Atomic Mass of Pb}) + 2 \times (\text{Atomic Mass of I})
]
[
\text{Molar Mass of PbI₂} = 207.2 \, \text{g/mol} + 2 \times 126.9 \, \text{g/mol}
]
[
\text{Molar Mass of PbI₂} = 207.2 \, \text{g/mol} + 253.8 \, \text{g/mol}
]
[
\text{Molar Mass of PbI₂} = 461.0 \, \text{g/mol}
]
📌 Note: Always use the most accurate atomic masses from the periodic table for precise calculations.
Why Molar Mass Matters

Understanding the molar mass of PbI₂ is vital for:
- Stoichiometry: Balancing chemical equations and determining reactant/product ratios.
- Solution Preparation: Calculating the amount of compound needed for a specific concentration.
- Experimental Accuracy: Ensuring precise measurements in laboratory experiments.
Quick Checklist for Calculating Molar Mass

- Step 1: Identify the chemical formula (PbI₂).
- Step 2: Look up atomic masses (Pb = 207.2 g/mol, I = 126.9 g/mol).
- Step 3: Multiply atomic masses by their respective coefficients.
- Step 4: Sum the values to get the molar mass (461.0 g/mol).
Applications of Lead(II) Iodide

Lead(II) iodide is used in:
- Perovskite Solar Cells: As a key component in photovoltaic technology.
- Photography: In the preparation of light-sensitive materials.
- Chemical Synthesis: As a reagent in various reactions.
What is the molar mass of lead(II) iodide?
+The molar mass of lead(II) iodide (PbI₂) is approximately 461.0 g/mol.
Why is molar mass important in chemistry?
+Molar mass is crucial for stoichiometry, solution preparation, and ensuring accurate experimental results.
What are the common uses of lead(II) iodide?
+Lead(II) iodide is used in solar cells, photography, and chemical synthesis.
In summary, calculating the molar mass of lead(II) iodide is a straightforward process that involves summing the atomic masses of its constituent elements. With a molar mass of 461.0 g/mol, PbI₂ plays a significant role in various scientific and industrial applications. Mastering this calculation ensures precision in your chemistry work, whether you’re in the lab or the classroom.
Related Keywords: molar mass calculation, lead iodide uses, chemical formula PbI₂, stoichiometry guide, perovskite solar cells.



