Understanding No Correlation Scatter Plots: A Clear Guide

Understanding No Correlation Scatter Plots: A Clear Guide
Scatter plots are powerful tools for visualizing relationships between two variables. However, not all scatter plots show a clear pattern. When data points appear randomly scattered without any discernible trend, it indicates no correlation. This guide will help you understand what no correlation scatter plots mean, how to interpret them, and their significance in data analysis. (data visualization, scatter plots, correlation analysis)
What is a No Correlation Scatter Plot?

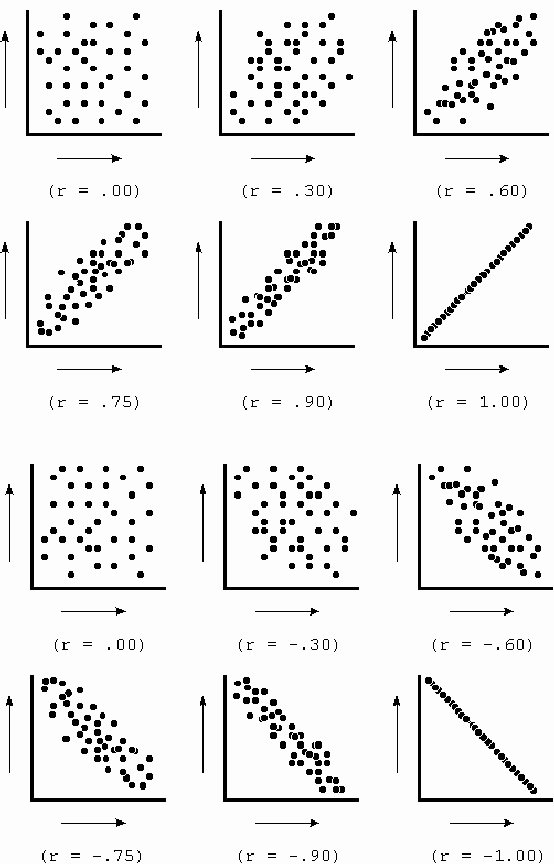
A no correlation scatter plot occurs when the data points on the graph do not follow any linear or nonlinear pattern. This suggests that changes in one variable do not predict changes in the other. In statistical terms, the correlation coefficient (e.g., Pearson’s r) is close to 0, indicating no relationship between the variables. (correlation coefficient, Pearson’s r, no relationship)
Key Characteristics of No Correlation Scatter Plots

Identifying a no correlation scatter plot is straightforward if you know what to look for:
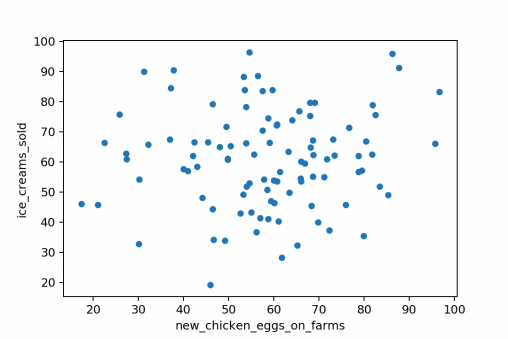
- Random Scatter: Data points appear scattered without forming any clear line or curve.
- No Trend: There is no upward, downward, or nonlinear trend visible.
- Correlation Near Zero: The correlation coefficient is close to 0, confirming no relationship.
📊 Note: Randomness in data doesn’t always mean the variables are unrelated. External factors or hidden variables might still influence the relationship.
Why No Correlation Matters
Understanding no correlation is crucial for accurate data interpretation. It helps you avoid making incorrect assumptions about relationships between variables. For example, if you’re analyzing sales data and find no correlation between advertising spend and revenue, it suggests that advertising might not directly impact sales. (data interpretation, variable relationships, sales analysis)
How to Create and Analyze No Correlation Scatter Plots

Creating a scatter plot is simple with tools like Excel, Python, or R. Here’s a basic checklist:
- Collect Data: Gather data for two variables.
- Plot the Data: Use a scatter plot tool to visualize the data points.
- Calculate Correlation: Use a statistical tool to compute the correlation coefficient.
- Interpret Results: If the plot shows random scatter and the correlation is near 0, conclude no correlation.
| Tool | Best For |
|---|---|
| Excel | Beginners and quick analysis |
| Python (Matplotlib) | Advanced customization and large datasets |
| R (ggplot2) | Statistical analysis and visualization |
Common Misinterpretations to Avoid
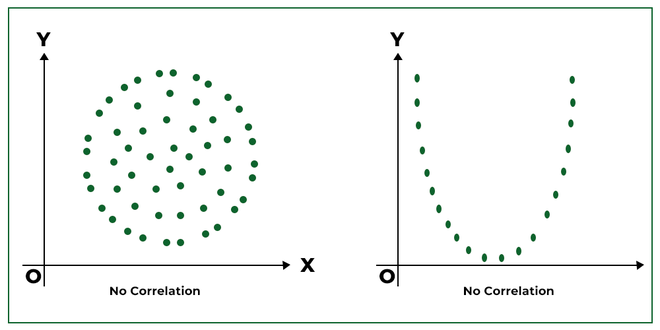
No correlation doesn’t mean the variables are entirely unrelated. Here are common mistakes to avoid:
- Assuming Causation: Lack of correlation doesn’t prove one variable doesn’t cause another.
- Ignoring Hidden Variables: Other factors might influence the relationship.
- Overlooking Nonlinear Relationships: Scatter plots might miss nonlinear patterns.
⚠️ Note: Always consider the context and explore further analysis if needed.
No correlation scatter plots are essential for understanding when variables don’t have a relationship. By recognizing their characteristics and avoiding misinterpretations, you can make more informed decisions in data analysis. Remember, randomness doesn’t always mean irrelevance—it’s a starting point for deeper exploration. (data analysis, informed decisions, variable relationships)
What does a no correlation scatter plot indicate?
+A no correlation scatter plot indicates that there is no linear or nonlinear relationship between the two variables being analyzed.
How is no correlation measured statistically?
+No correlation is typically measured using the correlation coefficient (e.g., Pearson’s r), which is close to 0 when there is no relationship.
Can variables still be related if a scatter plot shows no correlation?
+Yes, variables can still be related due to hidden factors or nonlinear relationships that scatter plots might not capture.