Effective Nursing Care Plan for Hypoxia: Quick Guide
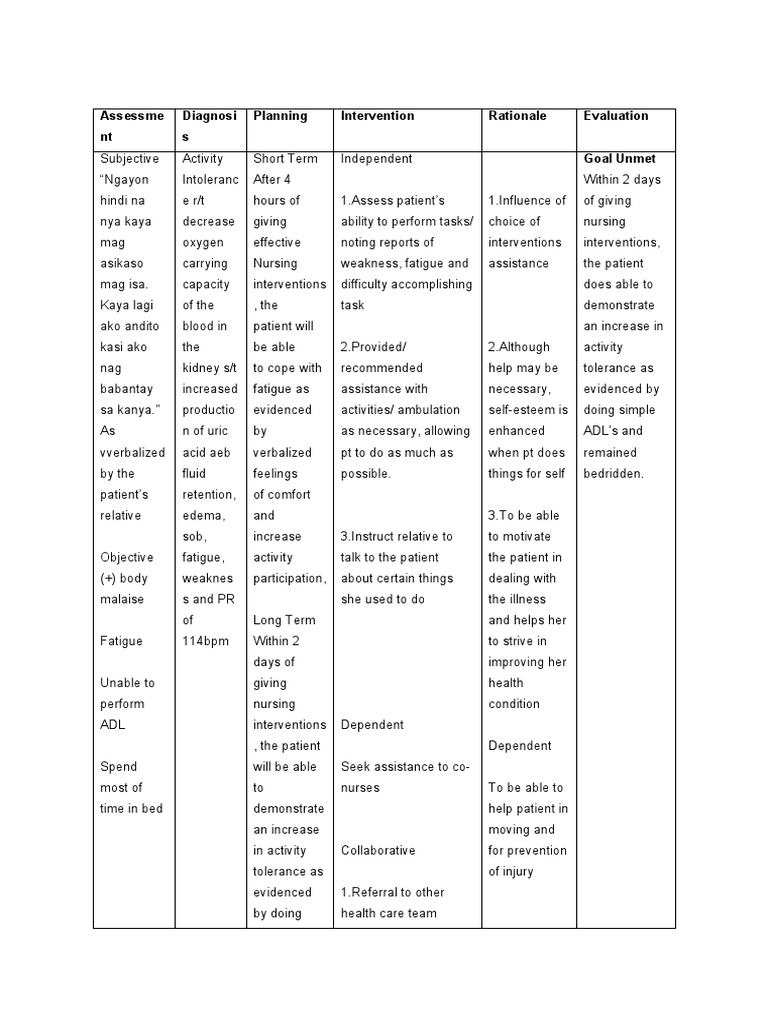
Effective Nursing Care Plan for Hypoxia: Quick Guide
Hypoxia, a condition where the body’s tissues receive inadequate oxygen, requires prompt and effective nursing care to prevent complications. Whether you’re a healthcare professional or a caregiver, understanding the nursing care plan for hypoxia is crucial for ensuring patient safety and recovery. This guide provides actionable steps, key interventions, and practical tips to manage hypoxia effectively.
Understanding Hypoxia: Causes and Symptoms

Hypoxia can result from various factors, including respiratory disorders, cardiovascular issues, or environmental conditions. Common symptoms include shortness of breath, confusion, rapid heartbeat, and bluish skin discoloration (cyanosis). Identifying these signs early is essential for timely intervention.
📌 Note: Always monitor vital signs closely, as hypoxia can escalate quickly if left untreated.
Key Components of a Nursing Care Plan for Hypoxia

1. Assessment and Monitoring
Begin by assessing the patient’s oxygen saturation levels using a pulse oximeter. Monitor respiratory rate, heart rate, and blood pressure regularly. Document any changes in symptoms or vital signs to guide further interventions.
2. Oxygen Therapy
Administer oxygen therapy as prescribed, ensuring the correct flow rate and delivery method (e.g., nasal cannula, mask). Aim for an oxygen saturation level of 92–96% for most patients.
3. Positioning and Comfort
Encourage the patient to sit upright or in a high Fowler’s position to improve oxygenation. Provide pillows or positioning aids for comfort and to reduce breathing effort.
4. Medication Management
Administer medications such as bronchodilators or diuretics as ordered to address underlying causes of hypoxia. Ensure compliance and monitor for side effects.
Practical Tips for Effective Hypoxia Management

- Educate Patients: Teach patients and caregivers about hypoxia, its causes, and the importance of adhering to the care plan.
- Promote Breathing Exercises: Encourage deep breathing and coughing exercises to improve lung function.
- Prevent Complications: Watch for signs of respiratory distress or infection and report them immediately.
📌 Note: Avoid overexertion in patients with hypoxia, as it can worsen oxygen deprivation.
Checklist for Hypoxia Nursing Care

- [ ] Assess oxygen saturation and vital signs regularly.
- [ ] Administer oxygen therapy as prescribed.
- [ ] Position the patient for optimal breathing.
- [ ] Monitor medication effectiveness and side effects.
- [ ] Educate the patient and family on hypoxia management.
Final Thoughts

Managing hypoxia requires a systematic approach, combining assessment, intervention, and education. By implementing this nursing care plan for hypoxia, you can improve patient outcomes and prevent complications. Stay vigilant, monitor closely, and collaborate with the healthcare team for the best results.
What are the early signs of hypoxia?
+Early signs include shortness of breath, rapid breathing, confusion, and bluish lips or nails (cyanosis).
How is oxygen therapy administered for hypoxia?
+Oxygen therapy is administered via nasal cannula, mask, or ventilator, depending on the severity of hypoxia.
Can hypoxia be prevented?
+While not always preventable, managing underlying conditions like COPD or heart disease can reduce the risk of hypoxia.
Related Keywords: nursing care plan for hypoxia, hypoxia management, oxygen therapy, respiratory care, patient education.


