What is Oncotic Pressure of Plasma? Understanding Plasma Oncotic Pressure Basics Key Role of Oncotic Pressure in Plasma Plasma Oncotic Pressure Explained Simply How Oncotic Pressure Affects Plasma Function Oncotic Pressure: Plasma’s Hidden Force Essential Guide to Plasma Oncotic Pressure
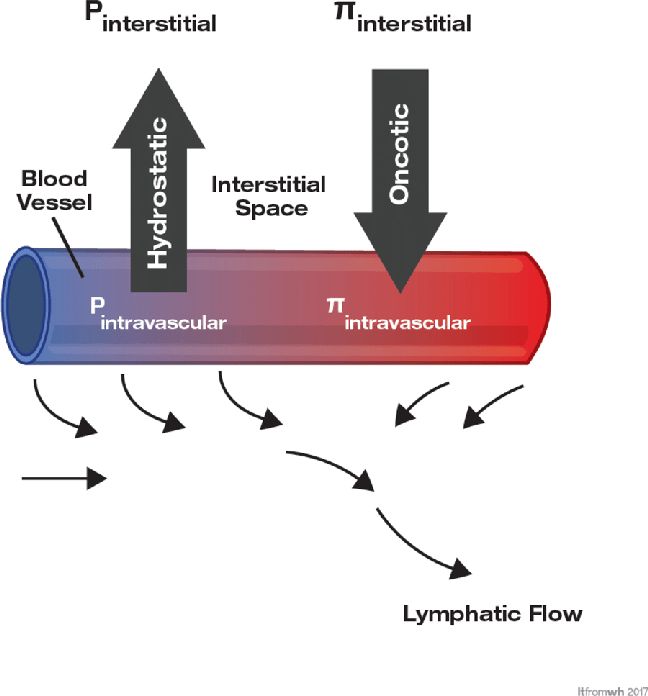
Plasma oncotic pressure, often referred to as colloid osmotic pressure, is a critical yet lesser-known force that plays a vital role in maintaining fluid balance within the body. It is the pressure exerted by proteins in the blood plasma, primarily albumin, which helps retain fluids within the circulatory system. This force is essential for preventing excessive fluid leakage into surrounding tissues, ensuring proper blood volume, and supporting overall vascular health. Understanding oncotic pressure is key to grasping how the body maintains homeostasis, especially in conditions like edema, dehydration, or kidney disease.
Understanding Plasma Oncotic Pressure Basics

Oncotic pressure is generated by large molecules, such as albumin and globulins, that cannot easily cross blood vessel walls. These proteins create an osmotic gradient, pulling water and small molecules back into the bloodstream. This mechanism is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the vascular system and preventing fluid accumulation in tissues.
💡 Note: Low oncotic pressure can lead to edema, while high levels may indicate dehydration or protein abnormalities.
Key Role of Oncotic Pressure in Plasma

The primary role of oncotic pressure is to balance hydrostatic pressure, which tends to push fluids out of blood vessels. Together, these forces regulate fluid distribution between the vascular and interstitial compartments. Oncotic pressure also influences nutrient and waste transport, ensuring that essential substances remain in the bloodstream for delivery to tissues.
Plasma Oncotic Pressure Explained Simply

Think of oncotic pressure as a “magnet” for water within blood vessels. Proteins like albumin act as anchors, preventing fluid from escaping into surrounding tissues. Without sufficient oncotic pressure, fluids would leak out, causing swelling and compromising blood volume.
How Oncotic Pressure Affects Plasma Function

Oncotic pressure directly impacts plasma function by:
- Maintaining Blood Volume: Ensures enough fluid stays in the circulatory system.
- Preventing Edema: Stops excessive fluid buildup in tissues.
- Supporting Nutrient Transport: Keeps proteins and nutrients in the bloodstream for distribution.
Oncotic Pressure: Plasma’s Hidden Force

Often overlooked, oncotic pressure is a silent guardian of vascular health. It works behind the scenes to keep fluids in balance, supporting vital functions like oxygen delivery and waste removal. Without it, the body’s fluid dynamics would collapse, leading to severe health issues.
Essential Guide to Plasma Oncotic Pressure
To maintain optimal oncotic pressure:
- Monitor Protein Levels: Ensure adequate protein intake, especially albumin.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports fluid balance.
- Manage Health Conditions: Conditions like liver disease or kidney issues can affect oncotic pressure.
| Factor | Effect on Oncotic Pressure |
|---|---|
| High Albumin Levels | Increases oncotic pressure |
| Low Albumin Levels | Decreases oncotic pressure |
| Dehydration | May increase oncotic pressure temporarily |

In summary, oncotic pressure is a fundamental force in plasma function, ensuring fluid balance and vascular health. By understanding its role and maintaining protein levels, you can support your body’s natural mechanisms for optimal health.
What causes low oncotic pressure?
+Low oncotic pressure is often caused by low albumin levels, liver disease, kidney disease, or malnutrition.
How is oncotic pressure measured?
+Oncotic pressure is measured using a colloid osmometer, which calculates the pressure exerted by plasma proteins.
Can dehydration affect oncotic pressure?
+Yes, dehydration can temporarily increase oncotic pressure as blood volume decreases, concentrating plasma proteins.
(plasma oncotic pressure,colloid osmotic pressure,fluid balance in plasma)



