Understanding Coefficient of Friction Units: A Quick Guide
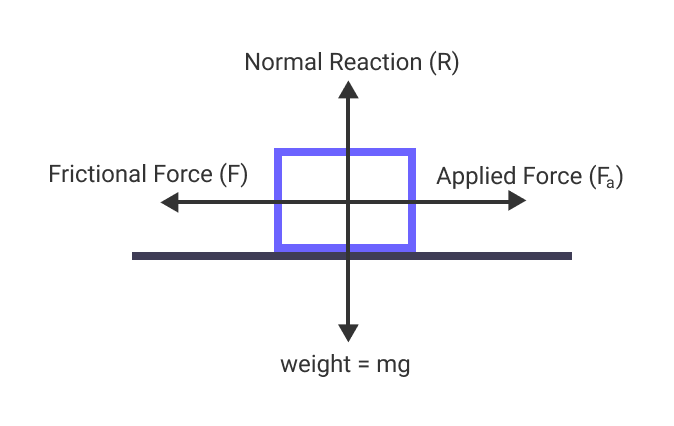
The coefficient of friction (COF) is a critical concept in physics and engineering, measuring the resistance to motion between two surfaces in contact. Whether you’re designing machinery, selecting materials, or simply curious about how objects interact, understanding COF units is essential. This guide breaks down the basics, ensuring you grasp the concept quickly and efficiently.
What is the Coefficient of Friction?

The coefficient of friction is a dimensionless scalar value that describes the ratio of the frictional force between two bodies and the force pressing them together. It’s represented as μ (mu) and is categorized into two types:
- Static Coefficient of Friction (μs): Measures friction when objects are at rest.
- Kinetic Coefficient of Friction (μk): Measures friction when objects are in motion.
📌 Note: The COF is always a positive value, typically between 0 and 1, though it can exceed 1 for certain materials.
Units of Coefficient of Friction
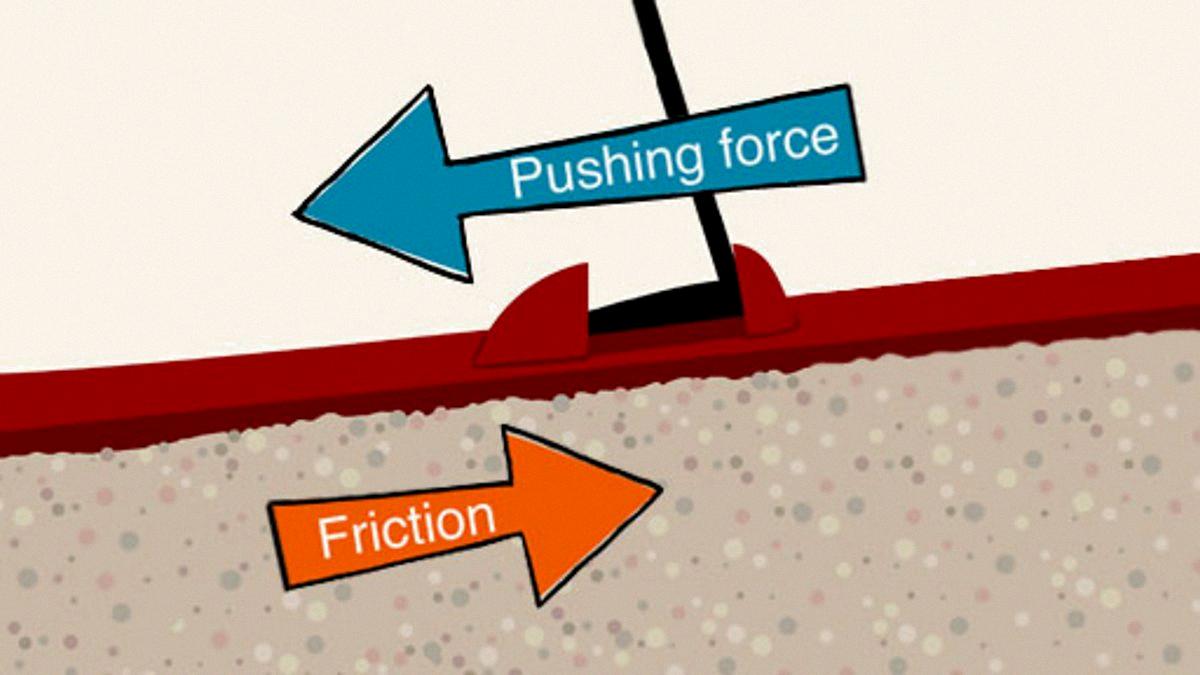
One common misconception is that the coefficient of friction has units. In reality, it’s a dimensionless quantity, meaning it has no units. This is because it’s derived from the ratio of two forces (frictional force and normal force), both measured in Newtons (N), which cancel each other out.
| Parameter | Units |
|---|---|
| Frictional Force (F) | Newtons (N) |
| Normal Force (N) | Newtons (N) |
| Coefficient of Friction (μ) | Dimensionless |

Why Understanding COF Units Matters

Grasping the concept of COF units is crucial for:
- Material Selection: Choosing the right materials for specific applications.
- Safety Standards: Ensuring machinery and equipment operate safely.
- Efficiency: Minimizing energy loss due to friction in mechanical systems.
How to Calculate Coefficient of Friction

The formula for COF is straightforward:
[
\mu = \frac{F}{N}
]
Where:
- F = Frictional force
- N = Normal force
📌 Note: Always ensure forces are measured in the same units (e.g., Newtons) for accurate calculations.
Practical Applications of COF

Understanding COF is vital in industries like:
- Automotive: Designing tires and brake systems.
- Construction: Selecting materials for flooring and roofing.
- Manufacturing: Optimizing machinery for efficiency and durability.
Key Takeaways
- The coefficient of friction is dimensionless and has no units.
- It’s calculated as the ratio of frictional force to normal force.
- COF is essential for material selection, safety, and efficiency in various industries.
Checklist for Understanding COF
- Define COF: Ratio of frictional force to normal force.
- Identify Types: Static (μs) and kinetic (μk).
- Confirm Units: Always dimensionless.
- Apply Formula: Use ( \mu = \frac{F}{N} ) for calculations.
What are the units of the coefficient of friction?
+The coefficient of friction is dimensionless and has no units.
How is the coefficient of friction calculated?
+It’s calculated as the ratio of frictional force (F) to normal force (N): \mu = \frac{F}{N} .
Why is the coefficient of friction important?
+It’s crucial for material selection, safety, and efficiency in engineering and industrial applications.
Understanding the coefficient of friction and its units is fundamental for anyone working with materials, machinery, or physics. By mastering this concept, you’ll make informed decisions and optimize performance in various applications. Whether you’re a student, engineer, or enthusiast, this quick guide has you covered. coefficient of friction calculation,friction units,material science,engineering basics,physics fundamentals.


