What is a Lipid Monomer?
Lipids are essential molecules that play a crucial role in biological systems, from energy storage to cell membrane structure. But what exactly is a lipid monomer? In simple terms, a lipid monomer is the basic building block of more complex lipid molecules. Understanding these monomers is key to grasping how lipids function in our bodies and in various industries, such as pharmaceuticals and food science. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious, this guide will break down the concept of lipid monomers in an easy-to-follow manner. (lipid structure, biological molecules, fatty acids)
What is a Lipid Monomer?

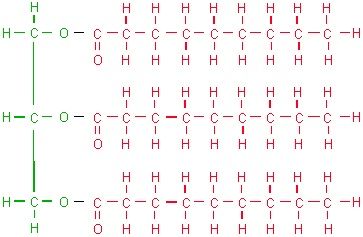
A lipid monomer is the simplest unit that makes up larger lipid structures. Unlike polymers, which are long chains of repeating units, monomers are single molecules. In the case of lipids, the primary monomers are fatty acids and glycerol. These molecules combine to form more complex lipids like triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids. (fatty acids, glycerol, lipid synthesis)
Types of Lipid Monomers
Lipid monomers can be broadly categorized into two main types:
- Fatty Acids: These are long chains of hydrocarbon molecules with a carboxyl group (-COOH) at one end. They are the primary components of fats and oils. (fatty acids, saturated fats, unsaturated fats)
- Glycerol: A small organic molecule with three hydroxyl (-OH) groups, glycerol acts as the backbone for many lipids, including triglycerides. (glycerol, triglycerides, lipid metabolism)
How Lipid Monomers Form Complex Lipids

Lipid monomers combine through a process called esterification, where fatty acids attach to glycerol molecules. For example, three fatty acids bonded to one glycerol molecule form a triglyceride, the most common type of fat in our diet. This process is fundamental to lipid synthesis and function. (esterification, triglycerides, lipid function)
Importance of Lipid Monomers
Lipid monomers are vital for several reasons:
- Energy Storage: Fats, composed of lipid monomers, are a dense source of energy for the body. (energy storage, metabolic processes)
- Cell Membrane Structure: Phospholipids, derived from fatty acids and glycerol, form the basis of cell membranes. (cell membrane, phospholipids)
- Hormone Production: Steroid hormones, such as cholesterol, are synthesized from lipid monomers. (hormone production, cholesterol)
💡 Note: While lipid monomers are essential, excessive consumption of certain types, like saturated fatty acids, can lead to health issues such as cardiovascular disease.
| Monomer | Function |
|---|---|
| Fatty Acids | Energy storage, cell membrane structure |
| Glycerol | Backbone for triglycerides and phospholipids |
Key Takeaways

To summarize, lipid monomers like fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of complex lipids. They play critical roles in energy storage, cell structure, and hormone production. Here’s a quick checklist to remember:
- Understand the difference between lipid monomers (fatty acids, glycerol) and polymers.
- Recognize the importance of esterification in lipid synthesis.
- Appreciate the roles of lipids in energy storage, cell membranes, and hormone production.
What are the main types of lipid monomers?
+The main types of lipid monomers are fatty acids and glycerol. (fatty acids, glycerol)
How do lipid monomers form triglycerides?
+Triglycerides are formed when three fatty acids attach to one glycerol molecule through esterification. (esterification, triglycerides)
Why are lipid monomers important in biology?
+Lipid monomers are crucial for energy storage, cell membrane structure, and hormone production. (energy storage, cell membrane, hormone production)
In conclusion, lipid monomers are the foundation of lipid molecules, playing indispensable roles in biology and industry. By understanding these basic units, we can better appreciate the complexity and importance of lipids in our daily lives. Whether you’re studying biochemistry or exploring lipid-based products, this knowledge is a valuable starting point. (lipid metabolism, biochemical pathways, lipid-based products)

