Understanding Spring Constant Units: A Quick Guide

<!DOCTYPE html>
Understanding the spring constant units is essential for anyone working with springs, whether in engineering, physics, or everyday applications. The spring constant, denoted as ( k ), measures a spring’s stiffness and is crucial for calculating its force, displacement, and potential energy. This guide breaks down the units, their significance, and practical applications, ensuring you grasp the concept effortlessly.
What Are Spring Constant Units?

The spring constant is measured in units of force per unit length. In the International System of Units (SI), the standard unit for the spring constant is the Newton per meter (N/m). This unit indicates how much force is required to stretch or compress a spring by one meter. For example, a spring with a constant of ( 200 \, \text{N/m} ) will exert 200 Newtons of force when stretched or compressed by one meter.
Why Are Spring Constant Units Important?
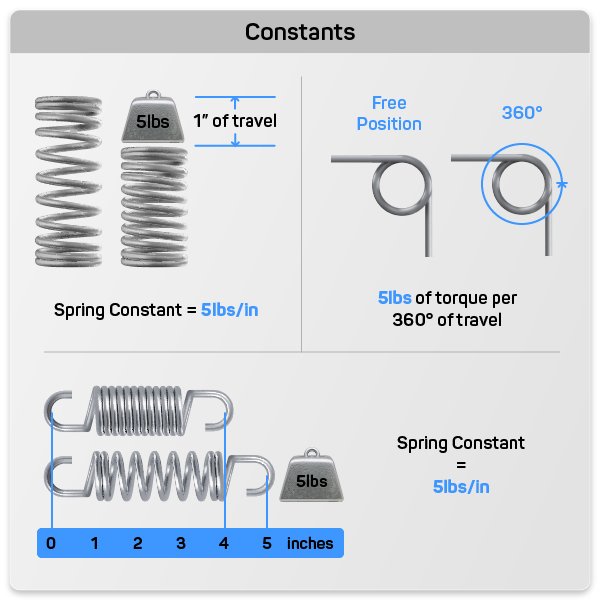
Understanding spring constant units is vital for several reasons. First, it helps in designing systems that involve springs, such as suspension systems in vehicles or mechanical watches. Second, it ensures accuracy in calculations related to Hooke’s Law, which states that the force exerted by a spring is directly proportional to its displacement. Finally, knowing the units aids in selecting the right spring for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
How to Calculate Spring Constant

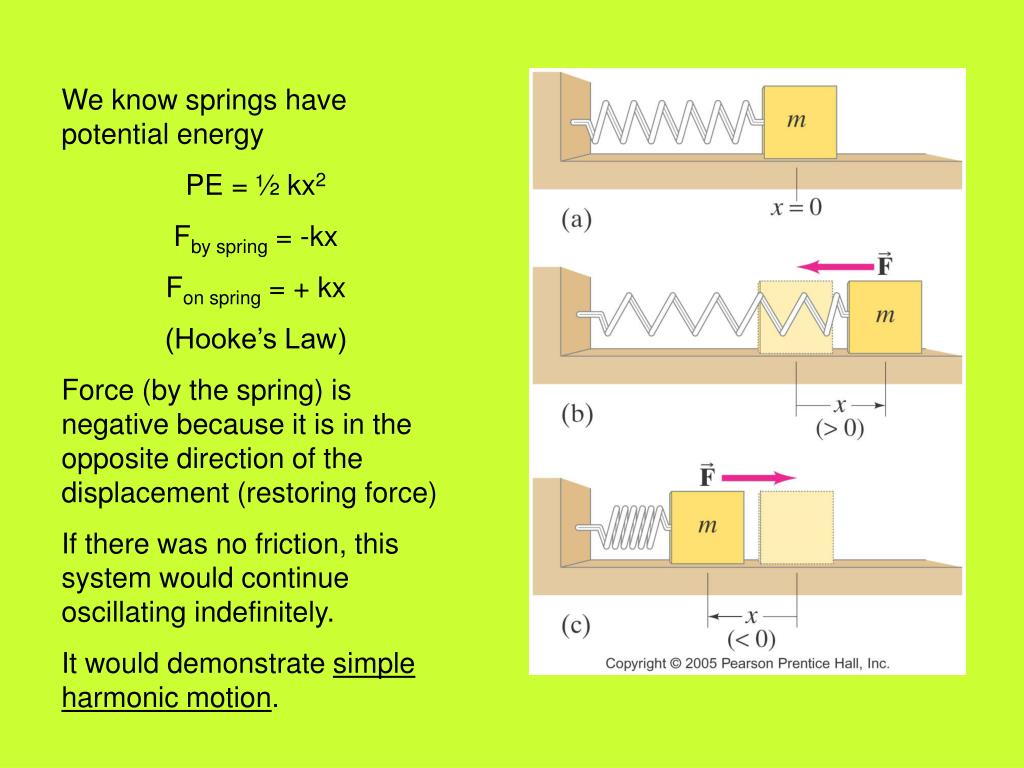
The spring constant ( k ) can be calculated using the formula derived from Hooke’s Law:
( F = -kx )
Where:
- ( F ) = Force applied to the spring (in Newtons, N)
- ( k ) = Spring constant (in N/m)
- ( x ) = Displacement of the spring (in meters, m)
To find ( k ), rearrange the formula:
( k = \frac{F}{x} )
📌 Note: Ensure consistent units when calculating the spring constant to avoid errors.
Common Units for Spring Constant

While N/m is the SI unit, other units are used depending on the context:
| Unit | Description |
|---|---|
| N/m | Newton per meter (SI unit) |
| lbf/in | Pound-force per inch (Imperial unit) |
| kgf/m | Kilogram-force per meter (Metric unit) |
Practical Applications of Spring Constant Units

The spring constant units play a critical role in various fields:
- Automotive Industry: Designing suspension systems for smooth rides.
- Mechanical Engineering: Creating precise mechanisms in clocks and machines.
- Physics Experiments: Studying simple harmonic motion and energy storage.
Checklist for Working with Spring Constant Units
- Verify the units of force and displacement before calculating the spring constant.
- Use the correct unit (e.g., N/m, lbf/in) based on the application.
- Test the spring’s stiffness to ensure it meets design requirements.
- Refer to Hooke’s Law for accurate force and displacement calculations.
Mastering spring constant units is key to working effectively with springs in any field. Whether you’re an engineer, student, or enthusiast, this knowledge ensures precision and reliability in your projects. (spring constant calculation,Hooke’s Law,spring stiffness)
What is the SI unit of the spring constant?
+The SI unit of the spring constant is Newton per meter (N/m).
How does the spring constant affect a spring’s behavior?
+A higher spring constant indicates a stiffer spring, requiring more force to deform it.
Can the spring constant change over time?
+Yes, factors like material fatigue or temperature changes can alter the spring constant.