Who Discovered the Proton? Unveiling the Scientific Breakthrough
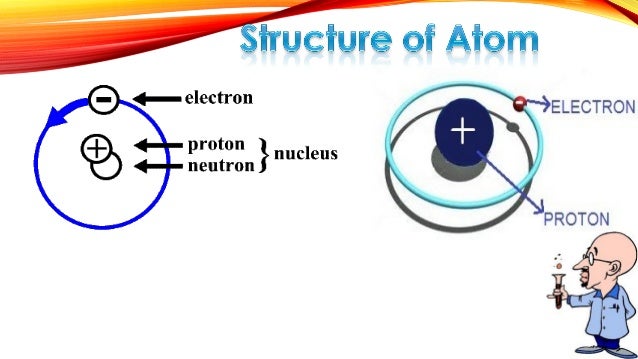
The discovery of the proton marked a pivotal moment in the history of science, reshaping our understanding of atomic structure. But who discovered the proton? This question leads us to the groundbreaking work of Ernest Rutherford, whose experiments in the early 20th century unveiled this subatomic particle. In this post, we’ll explore the journey of this scientific breakthrough, its significance, and its impact on modern physics, all while addressing key queries like proton discovery timeline, Rutherford’s gold foil experiment, and subatomic particles history.
The Pioneer Behind the Proton Discovery

Ernest Rutherford, a New Zealand-born physicist, is credited with the discovery of the proton. In 1919, Rutherford conducted a series of experiments that led to the identification of this positively charged particle. His work built upon earlier discoveries about atomic structure, including the existence of electrons and the nucleus.
💡 Note: Rutherford’s discovery was a result of his gold foil experiment, which also confirmed the nuclear model of the atom.
Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment Explained

The gold foil experiment, performed in 1911, was a turning point in atomic physics. Rutherford and his team directed alpha particles at a thin sheet of gold foil. Most particles passed straight through, but some were deflected at large angles. This led Rutherford to propose the existence of a dense, positively charged nucleus at the atom’s center.
- Alpha particles: Helium nuclei used in the experiment.
- Gold foil: Chosen for its thinness and malleability.
- Key observation: Deflection of particles indicated a concentrated positive charge.
From Discovery to Modern Applications

The discovery of the proton laid the foundation for modern nuclear physics. Today, protons are essential in fields like medicine (proton therapy), energy (nuclear reactors), and research (particle accelerators). Understanding protons has also led to advancements in quantum mechanics and elementary particle physics.
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Medicine | Proton therapy for cancer treatment |
| Energy | Nuclear power generation |
| Research | Particle accelerators like the Large Hadron Collider |

Checklist: Key Takeaways
- Ernest Rutherford discovered the proton in 1919.
- The gold foil experiment confirmed the atomic nucleus.
- Protons are vital in medicine, energy, and research.
The discovery of the proton by Ernest Rutherford revolutionized our understanding of matter. From his pioneering experiments to modern applications, protons remain a cornerstone of science. Whether you’re exploring atomic structure, nuclear physics, or scientific history, this breakthrough continues to inspire curiosity and innovation.
Who discovered the proton?
+
Ernest Rutherford discovered the proton in 1919 through his experiments.
What is the gold foil experiment?
+
It was an experiment by Rutherford that demonstrated the existence of a dense, positively charged atomic nucleus.
How are protons used today?
+
Protons are used in proton therapy, nuclear energy, and particle physics research.



