Nitrile Hydrolysis Mechanism Explained: A Simple Guide
Understanding the nitrile hydrolysis mechanism is crucial for chemists, researchers, and students alike. This process involves the conversion of nitriles into carboxylic acids or amides, depending on the reaction conditions. Whether you're exploring organic chemistry, working in pharmaceutical research, or studying chemical synthesis, grasping this mechanism is essential. In this guide, we’ll break down the nitrile hydrolysis process step-by-step, making it accessible and easy to comprehend. Let’s dive into the world of chemical reactions and unravel the intricacies of nitrile hydrolysis.
What is Nitrile Hydrolysis?

Nitrile hydrolysis is a fundamental chemical reaction where a nitrile group (C≡N) is converted into a carboxylic acid (R-COOH) or an amide (R-CONH₂). This reaction is widely used in organic synthesis, particularly in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and fine chemicals. The process typically requires a catalytic agent, such as acid or base, to facilitate the transformation. Understanding the mechanism helps in optimizing reaction conditions and predicting product outcomes.
The Nitrile Hydrolysis Mechanism Explained

The nitrile hydrolysis mechanism involves several steps, depending on the catalyst used. Below is a simplified breakdown:
Step 1: Protonation of the Nitrile Group
In an acidic environment, the nitrile group is protonated, forming an iminium ion. This step is crucial for activating the nitrile towards nucleophilic attack by water.
Step 2: Nucleophilic Attack by Water
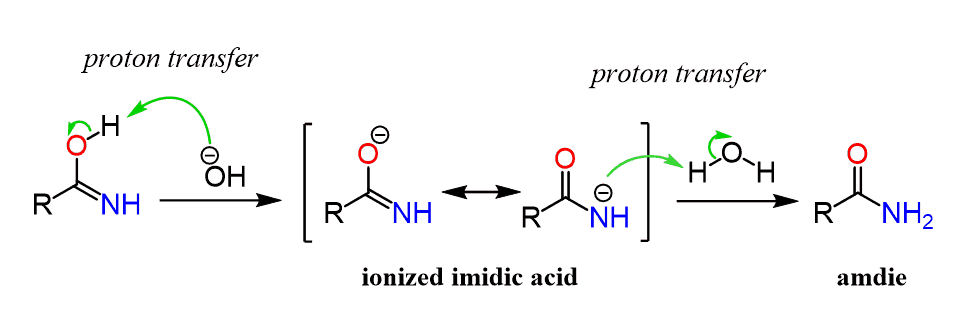
Water molecules act as a nucleophile, attacking the protonated nitrile. This leads to the formation of an intermediate, known as an amidate ion.
Step 3: Deprotonation and Product Formation
The amidate ion is deprotonated, resulting in the formation of a carboxylic acid or an amide, depending on the reaction conditions. This final step completes the nitrile hydrolysis process.
📌 Note: The choice of catalyst (acid or base) significantly influences the final product. Acidic conditions favor carboxylic acid formation, while basic conditions promote amide formation.
Factors Affecting Nitrile Hydrolysis

Several factors impact the efficiency and outcome of nitrile hydrolysis. These include:
- Catalyst Type: Acidic or basic catalysts determine the product formed.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures generally accelerate the reaction but may lead to side reactions.
- Solvent Choice: Polar solvents like water or alcohol enhance reactivity.
- Reaction Time: Longer reaction times can improve yield but may also increase side product formation.
Applications of Nitrile Hydrolysis

Nitrile hydrolysis plays a vital role in various industries, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
- Polymers: Production of nylon and other polyamides.
- Fine Chemicals: Manufacturing of specialty chemicals and intermediates.
Nitrile Hydrolysis Mechanism Checklist

- Understand the role of catalytic agents in the reaction.
- Identify the steps: protonation, nucleophilic attack, and deprotonation.
- Consider factors like temperature, solvent, and reaction time for optimal results.
- Apply knowledge to pharmaceutical, polymer, and fine chemical industries.
In summary, the nitrile hydrolysis mechanism is a cornerstone of organic chemistry, enabling the synthesis of essential compounds like carboxylic acids and amides. By understanding the steps involved and the factors influencing the reaction, chemists can optimize processes for various applications. Whether you're a student, researcher, or industry professional, mastering this mechanism opens doors to innovative chemical solutions. (nitrile hydrolysis, organic chemistry, chemical synthesis)
What is the primary product of nitrile hydrolysis in acidic conditions?
+In acidic conditions, the primary product of nitrile hydrolysis is a carboxylic acid.
Can nitrile hydrolysis occur without a catalyst?
+While possible, nitrile hydrolysis is significantly slower without a catalytic agent, making catalysts essential for practical applications.
How does temperature affect nitrile hydrolysis?
+Higher temperatures accelerate the reaction but may lead to side reactions or decomposition of intermediates.



